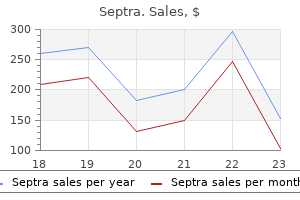
Septra dosages: 480 mg
Septra packs: 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Buy 480mg septra otc
The click corresponds to the prolapsing leaflets, and the systolic murmur is variable and dependent on the diploma of mitral regurgitation. Having the affected person perform a Valsalva maneuver will increase intrathoracic pressures, thereby decreasing venous return and end-diastolic volume. This ends in an earlier click on nearer to the first heart sound and a chronic murmur. The click on may be heard later in systole together with a chronic murmur if venous return or end-diastolic volume is increased. Atypical chest pain is maybe associated to papillary muscle pressure from excessive pulling on the left ventricular wall from prolapsed leaflets within the left atrium. If chordae tendinae rupture has occurred, the affected person might undergo severe mitral regurgitation, pulmonary edema, and severe shortness of breath. On auscultation, a mid-systolic click on followed later by a systolic murmur heard Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology the mitral valve (or bicuspid valve) is composed of two mitral leaflets (or cusps) anchored by the mitral annulus. The anteromedial and the posterolateral leaflets of the mitral valve collectively resemble a miter (a hat worn by bishops), therefore its name. During systole, the left ventricle contracts and the mitral valve leaflets are apposed passively on account of the elevated left ventricular pressure. Valve prolapse is prevented by the chordae tendinae, that are inelastic fibrous bands which are anchored proximally to the papillary muscle tissue and distally to the valve cusps. The papillary muscles are finger-like projections emanating from the wall of the left ventricle activated to contract and tense the chordae tendinae at the appropriate second within the cardiac cycle to prevent the mitral valve leaflets from prolapsing. Each mitral valve leaflet is composed of three layers of tissue: the atrialis, fibrosa, and spongiosa. This weakens the leaflet and surrounding tissue, leading to elevated leaflet area and elongation of the chordae tendinae. Frontal radiograph of the chest demonstrates elevated interstitial lung markings in the apices bilaterally with a small right pleural effusion (arrowhead) and outstanding hilar vascular markings indicative of pulmonary edema (arrows). Imaging of the valve is typically carried out using transthoracic or transesophgeal echocardiography. A flail leaflet ranges from eversion of the leaflet tip to chordal rupture, which allows for unrestricted leaflet movement and mitral regurgitation. Mitral regurgitation may be visualized and graded utilizing shade Doppler imaging on routine echocardiography. Note the presence of pectus excavatum, a recognized danger issue for creating mitral valve prolapse (white arrow). Endothelial harm from turbulent flow makes these sufferers extra prone to infective endocarditis due to transient bacteremia during dental procedures, necessitating antibiotic prophylaxis earlier than main dental procedures. Note the presence of a small dephasing jet (white arrow) that appears as a "puff of smoke" representing mitral regurgitation. Unlike involvement of the mitral valve in rheumatic coronary heart illness, the commissures of the mitral leaflets are normally spared. Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology the mitral annulus is a C-shaped fibrous skeleton located on the junction of the left atrium and left ventricle. It anchors the mitral leaflets, assisting in leaflet apposition by contracting and expanding during systole and diastole, respectively. The annulus offers its structural support to the mitral leaflets along the medial, posterior, and lateral portions of the valve. Anteriorly, the center section of the anterior leaflet is in fibrous continuity with the posterior aortic root with out intervening annular tissue, which explains the C-shape of the mitral annulus. Endothelial injury in areas of mechanical stress, such as between the mitral annulus and ventricular myocardium, leads to focal accumulation of oxidized lipids that function a nidus for chronic irritation. The development of calcification may be accelerated by altered mineral metabolism, as seen in kidney illness. Echocardiography demonstrates an echodense shelf-like structure involving the mitral annulus with associated acoustic shadowing. Patients could often present with complications such as mitral stenosis, mitral regurgitation, infective endocarditis, atrial arrhythmias, coronary heart block, and/or an embolic occasion. Mitral annular calcification: a marker of severe coronary artery disease in patients under 65 years old. Mitral annular calcification predicts cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: the Framingham Heart Study.
Diseases
- TRAPS
- Neutropenia, severe chronic
- Ulna metaphyseal dysplasia syndrome
- Diethylstilbestrol antenatal infection
- Cogan Reese syndrome
- Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase deficiency
- Corneal crystals myopathy neuropathy
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency
- Laryngeal neoplasm
- Troyer syndrome
Purchase septra american express
Fluoroscopy, notably in a cardiac catheterization lab, is used for real-time catheter floatation. As the catheter traverses the proper heart, pressures are measured in the proper atrium, proper ventricle, and pulmonary artery. In this technique, a recognized quantity bolus of cold fluid is injected into the best atrial port, and the change in temperature in the pulmonary artery is measured over time using the thermistor at the tip of the catheter. Continuous cardiac output measurements are attainable with newer catheters which have a heating filament, where dilution of heated blood is used for a similar calculation. The catheter should then curve by way of the proper ventricle and into the pulmonary trunk. The catheter tip should be in the main, right primary, or left primary pulmonary artery. Unless getting used to measure the wedge pressure, the balloon is always left deflated and the catheter is retracted into a major pulmonary artery. Failure to deflate the balloon could also be observed as a round area of lucency surrounding the catheter tip. Frontal (a) and lateral (b) radiographs of the chest of a affected person with a proper internal jugular Swan-Ganz (pulmonary artery) catheter. Note the course of the catheter via the superior vena cava, proper atrium, right ventricle, major pulmonary artery and its tip in the right primary pulmonary artery (arrow). Frontal radiograph of a Swan-Ganz (pulmonary artery) catheter getting into the center by way of a femoral strategy. Note the catheter looped in the best atrium/inferior vena cava, with the tip probably in the left hepatic vein (arrow). The additional femoral line with tip in the right atrium is a venous pacing wire (arrowhead). Common Variants Currently, Swan-Ganz catheters can be found with further features. Note that the tip is roughly 50% of the space across the proper hemithorax (white arrow). Some include a proximal thermal filament for steady cardiac output measurements (in conjunction with the distal thermistor). Pulmonary artery catheters inserted by way of the femoral vein may have a different curve at its tip to allow simpler placement. Regardless of these modifications, similar position tips must be adopted, and related issues ought to be evaluated. Frontal radiograph of a Swan-Ganz (pulmonary artery) catheter that enters the center via a proper internal jugular strategy. Clinical Issues As with all invasive catheters, day by day assessment is really helpful given the continued risk of catheter-related an infection and thrombosis. This could lead to free perforation into the pleural area, recognized radiographically as a new unexplained ipsilateral pleural effusion, representing a hemothorax. Both of these scenarios might present with hemoptysis and, when extreme, could lead to asphyxiation. These require pressing or emergent surgery or endovascular coiling to cease the bleeding or prevent pseudoaneurysm rupture. Gross Definition Cardiovascular implantable electrical units are required for the care of a wide range of sufferers with cardiac abnormalities. Pacemakers deliver low-energy stimuli to treat bradyarrhythmias brought on by sinus node dysfunction or atrioventricular conduction abnormalities. Cardiac resynchronization gadgets are designed to deliver synchronous biventricular pacing in an attempt to attenuate morbidity and improve survival of patients with advanced coronary heart failure. The pulse generator consists of digital hardware, programmable software, and a battery with a 5- to 10-year life span. Pacemaker leads comprise conductor cables which would possibly be attached to the intracardiac electrodes, coated by numerous forms of insulation material, and have several sorts of fixation mechanisms on the lead tip. The most proximal portion of the lead incorporates the connecting pins, which are inserted into the heartbeat generator header. Very infrequently, leads are placed by way of an epicardial approach, usually within the setting of an open heart process. Indications for pacemaker placement include sick sinus syndrome, symptomatic sinus bradycardia, tachybrady syndrome, atrial fibrillation with sinus node dysfunction, and full atrioventricular block. Pulse generator placement is both subcutaneous or submuscular, most commonly in the pectoral area.
Buy cheap septra 480mg
Replacement with a tool that communicates on a different frequency could additionally be required. Radiofrequency catheter ablation this is typically undertaken within the electrophysiology lab for varied atrial and ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Reprogramming the device to an asynchronous mode will prevent this concern from arising. Therapeutic radiation Therapeutic radiation has a unique effect along with oversensing. Ionizing radiation can lead to random element failure and untimely battery depletion. Though the impact is cumulative, the mode of gadget failure is random and unpredictable. In rare instances, a newly placed contralateral system or generator repositioning utilizing lead extenders should be thought-about. If included in the radiation field, the gadget should be interrogated after every treatment; nevertheless, device malfunctions might typically turn out to be manifest late after radiation publicity. Damage may lead to sudden lack of output, alterations in programmed parameters, and fee runaway. Lithotripsy Lithotripsy has the potential to trigger pacing inhibition, triggered pacing at the upper price restrict, and activation of price modulation. Lithotripsy synchronized to the R wave is less frequently used these days, significantly as it can add to the size of the procedure. This mode should be strongly considered in these with significant ventricular irritability, as the synchronized pulses are less likely to end in ventricular arrhythmias. If the lithotripter is utilized in a synchronized mode, care must be taken to ensure that the pulses are synchronized to the R wave and not the P wave or atrial spike, which may end up in oversensing and ventricular pacing inhibition. In common, rate modulation must be disabled and consideration given to programming to an asynchronous mode, notably with pacemakerdependent sufferers. Patient components (pacemaker dependency, programmed parameters), procedural components (type of surgical procedure, whether or not cautery might be used), and system elements (battery life, chronicity of leads, magnet response) ought to all be considered. Recommendations to be used of a magnet throughout surgery or for device reprogramming should be individualized based on this. It is crucial to have tools for cardioversion/defibrillation and external pacing readily available; placement of pads for this purpose ought to be thought-about in most sufferers. Patients nearing finish of life or requesting withdrawal of remedy the device doctor could additionally be called upon to help in the management of patients nearing finish of life or requesting withdrawal of remedy. Recently, a multidisciplinary group developed an expert consensus statement that addresses these points. This knowledgeable refusal, a corollary of knowledgeable consent, is considered a private proper of the affected person. Deactivation of pacing would require reprogramming, whereas antitachycardia therapies may be deactivated by reprogramming or magnet application. Reprogramming the gadget to quicker charges for overdrive pacing, or utilizing the triggered mode with chest wall stimulation to "program in" additional stimuli, may show helpful. Some units enable for programmed stimulation in either chamber utilizing the programmer. In all instances, the intervention must be undertaken cautiously with defibrillator back-up. Diagnosis of myocardial ischemia/infarction within the pacemaker patient Device interrogation or reprogramming for analysis and treatment of arrhythmias the system physician may be called upon to terminate tachyarrhythmias acutely, preferably without the necessity for cardioversion or defibrillation. Some gadgets enable for momentary high-rate pacing to above 300 bpm, allowing for the pace termination of atrial flutter. T wave adjustments alone ought to be interpreted with caution on this setting because ventricular pacing might produce T wave abnormalities, which are persistent after the discontinuation of pacing (T wave memory). These information are generated from voluntary doctor reporting of system failures and post-market surveillance registries. Unfortunately, knowledge on the efficiency of any system mannequin are by no means complete as a end result of the voluntary nature of the registries, physician under-reporting of malfunctions, and failure to return out-of-service devices for evaluation (especially from deceased patients). Device producers may immediately concern security alerts (product notifications) as nicely. Whereas the producer could provide a non-invasive reprogramming technique to right or reduce the probability of some malfunctions, the physician is in any other case left to make complicated end result decisions for every patient with an affected gadget.
Generic septra 480 mg otc
The skin and subcutaneous tissue have been eliminated to show the deep fascia of the leg and dorsum of the foot. Thinner components of the plantar fascia have been eliminated, revealing the plantar digital vessels and nerves. A giant central and smaller medial and lateral compartments of the solely real are created by intermuscular septa that reach deeply from the plantar aponeurosis. Although the adductor hallucis resembles an analogous muscle of the palm that adducts the thumb, despite its name the adductor hallucis might be most lively in the course of the push-off section of stance in pulling the lateral four metatarsals toward the great toe, fixing the transverse arch of the foot, and resisting forces that may spread the metatarsal heads as weight and pressure are utilized to the forefoot (Table 5. The 2nd layer consists of the long flexor tendons and related muscles: 4 lumbricals and the quadratus plantae. The 3rd layer consists of the flexor of the little toe and the flexor and adductor of the good toe. The posterior tibial artery terminates as it enters the foot by dividing into the medial and lateral plantar arteries. Branching of the mother or father neurovascular buildings that give rise to plantar vessels and nerves. After coursing between and supplying the fibular muscles within the lateral compartment of the leg, the superficial fibular nerve emerges as a cutaneous nerve about two thirds of the greatest way down the leg. It then provides the pores and skin on the anterolateral aspect of the leg and divides into the medial and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves, which continue throughout the ankle to supply a lot of the skin on the dorsum of the foot. Its terminal branches are the dorsal digital nerves (common and proper) that offer the pores and skin of the proximal side of the medial half of the great toe and that of the lateral three and a half digits. It innervates this space as the 1st widespread dorsal (and then correct dorsal) digital nerve(s). The medial plantar nerve, the larger and extra anterior of the 2 terminal branches of the tibial nerve, arises deep to the flexor retinaculum. Its distribution to both skin and muscle tissue of the foot is comparable to that of the median nerve within the hand. The stage of junction of these branches is variable; it might be high (in the popliteal fossa), or low (proximal to heel). The dorsalis pedis artery begins halfway between the malleoli and runs anteromedially, deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum between the extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum longus tendons on the dorsum of the foot. The dorsalis pedis artery passes to the first interosseous area, where it divides into the 1st dorsal metatarsal artery and a deep plantar artery. The latter passes deeply between the heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscle to enter the solely real of the foot, the place it joins the lateral plantar artery to kind the deep plantar arch. The arcuate artery runs laterally throughout the bases of the lateral four metatarsals, deep to the extensor tendons, to attain the lateral aspect of the forefoot, where it might anastomose with the lateral tarsal artery to type an arterial loop. The medial and lateral plantar arteries are terminal branches of the posterior tibial artery. The deep plantar artery and perforating branches of the deep plantar arch provide anastomoses between the dorsal and the plantar arteries. Unlike the leg and thigh, nevertheless, the venous drainage of the foot is primarily to the most important superficial veins, each from the deep accompanying veins and different smaller superficial veins. These veins drain to the dorsal venous arch of the foot, proximal to which a dorsal venous community covers the remainder of the dorsum of the foot. The bigger superficial department of the medial plantar artery provides the pores and skin on the medial aspect of the sole and has digital branches that accompany digital branches of the medial plantar nerve, the extra lateral of which anastomose with medial plantar metatarsal arteries. As it crosses the foot, the deep plantar arch provides rise to 4 plantar metatarsal arteries; three perforating branches; and heaps of branches to the skin, fascia, and muscular tissues in the sole. The plantar metatarsal arteries divide close to the bottom of the proximal phalanges to form the plantar digital arteries, supplying adjacent digits (toes); the more medial metatarsal arteries are joined by superficial digital branches of the medial plantar artery. The lateral superficial lymphatic vessels drain the lateral aspect of the dorsum and sole of the foot. The fibularis brevis tendon can simply be traced to its attachment to the dorsal floor of the tuberosity on the base of the 5th metatarsal.
Berberis diversifolia (Oregon Grape). Septra.
- What other names is Oregon Grape known by?
- What is Oregon Grape?
- How does Oregon Grape work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Oregon Grape.
- Psoriasis.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96499
Buy cheap septra on-line
The radial neurovascular bundle- containing the radial artery, accompanying veins, and superficial radial nerve-courses along and defines the border between the anterior and the posterior forearm compartments (the vascular constructions serving both) deep to the brachioradialis. The deep radial nerve penetrates the supinator to be a part of the posterior interosseous artery in the airplane between the superficial and the deep extensors. Once positioned at the desired top and location relative to the body by actions at the shoulder and elbow, and the course of motion is established by pronation and supination of the forearm, the working place or attitude (tilt) of the hand is adjusted by motion on the wrist joint. Because of the significance of handbook dexterity in occupational and leisure actions, an excellent understanding of the structure and function of the hand is crucial for all individuals concerned in maintaining or restoring its actions: free motion, power greedy, precision dealing with, and pinching. Conversely, as flexion increases on the wrist, the grip turns into weaker and extra insecure. In a precision grip, the wrist and digits are held firmly by the lengthy flexor and extensor muscles, and the intrinsic hand muscular tissues perform fantastic actions of the digits. One makes use of the precision grip to maintain a coin to enable manipulation (D) and when pinching an object (E). Medial to this septum is the medial or hypothenar compartment, containing the hypothenar muscular tissues and bounded anteriorly by the hypothenar fascia. Lateral to this septum is the lateral or thenar compartment, containing the thenar muscular tissues and bounded anteriorly by the thenar fascia. Although most fascial compartments end at the joints, the midpalmar space is steady with the anterior compartment of the forearm through the carpal tunnel. Hypothenar muscular tissues in the hypothenar compartment: abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, and opponens digiti minimi. Short muscle tissue of the hand, the lumbricals, within the central compartment with the long flexor tendons. The palmar aponeurosis, a strong, well-defined part of the deep fascia of the palm, covers the soft tissues and overlies the long flexor tendons. When the palmaris longus is current, the palmar aponeurosis is the expanded tendon of the palmaris longus. The thenar house underlies the thenar compartment and is said distally to the synovial tendon sheath of the index finger and proximally to the common flexor sheath distal to the carpal tunnel. The pores and skin and subcutaneous tissue have been removed, as have a lot of the palmar aponeurosis and the thenar and hypothenar fasciae. Three thenar and three hypothenar muscle tissue connect to the flexor retinaculum and to the four marginal carpal bones united by the retinaculum. It flexes and rotates the first metacarpal medially on the carpometacarpal joint throughout opposition; this motion happens when choosing up an object. The palmaris brevis wrinkles the pores and skin of the hypothenar eminence and deepens the hollow of the palm, thereby aiding the palmar grip. The lumbricals flex the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints and lengthen the interphalangeal joints. Acting collectively, the dorsal and palmar interossei and the lumbricals produce flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension of the interphalangeal joints (the so-called Z-movement). These sheaths forestall the tendons from pulling away from the digits (bowstringing). The fibrous digital sheaths combine with the bones to kind osseofibrous tunnels through which the tendons cross to reach the digits. The tendons enter the central compartment of the hand and fan out to enter their respective digital synovial sheaths. Flexor tendons, widespread flexor sheath, fibrous digital sheaths, and synovial sheaths of digits. The ulnar and radial arteries and their branches present all of the blood to the hand. The superficial palmar arch, the primary termination of the ulnar artery, provides rise to three common palmar digital arteries that anastomose with the palmar metacarpal arteries from the deep palmar arch. The carpal bones are totally ossified on this teenage hand, but the epiphysial plates (growth plates) of the lengthy bones remain open. Superficial to the metacarpus, this network is extended proximally on the lateral side as the cephalic vein.
Order septra pills in toronto
Later in growth, the truncus arteriosis rotates and is divided by the aorticopulmonary septum to form the aorta and the principle pulmonary artery. Isolated unilateral absence of a pulmonary artery is believed to end result from involution of the proximal sixth aortic arch on the affected side. Absence of the right pulmonary artery is twice as common as absence of the left pulmonary artery, and left-sided absence is extra more probably to be associated with additional cardiovascular malformations, especially tetralogy of Fallot. Findings might embrace a small hemithorax, decreased rib spacing, ipsilateral hemidiaphragm elevation, ipsilateral mediastinal shift, and contralateral lung hyperinflation. Absence of the pulmonary artery leads to an absent hilar shadow and decreased vascular markings. Expiratory chest radiographs may be performed and will reveal no air trapping. Echocardiography and cross-sectional imaging are useful as second-line imaging modalities in suspected circumstances of absent pulmonary artery. Echocardiography can be utilized to affirm the diagnosis, exclude further cardiovascular malformations, and evaluate for the presence of pulmonary hypertension. Ventilation and perfusion research show attribute findings of absent perfusion and normal to mildly decreased ventilation with no delayed washout. Both pictures reveal volume loss in the proper lung and shift of the trachea, heart, and mediastinum toward the best. There is compensatory hyperinflation of the left lungs, which extend across midline. Conventional angiography has historically been thought-about the reference commonplace within the analysis of absent pulmonary artery and may establish collateral vessels supplying the lung with absent pulmonary artery. Conventional angiography is usually reserved to deal with sufferers with hemoptysis or used previous to revascularization surgical procedure to consider if hilar pulmonary arteries exist. In some sufferers, fibrotic modifications could be seen in the lung with absent pulmonary artery and could possibly be associated to recurrent infections. What Not to Miss Chest radiographs reveal a small hemithorax with decreased vascular markings. Ventilation and perfusion research show absent perfusion with normal to barely decreased air flow and no air trapping. A outstanding collateral vessel (arrow) arises from the celiac artery and extends superiorly to the proper lung. Enlarged bronchial artery and collateral vessels may additionally be seen in the best hilum (arrows). Foreign body Lobar atelectasis Status post-lobectomy Additional cardiovascular malformations are frequent, particularly with absence of the left pulmonary artery. Differential Diagnosis the principle differential consideration is Swyer-James syndrome, which is thought to result from a childhood viral infection causing bronchiolar obliteration and subsequent decreased blood move to the affected lung. Chest radiographs reveal a unilateral hyperlucent lung, and lung volumes could also be decreased, normal, or elevated. Patients identified through the first year of life often present with pulmonary hypertension and coronary heart failure. Pulmonary hypertension could additionally develop later in life or be unmasked by conditions corresponding to pregnancy and high-altitude pulmonary edema. Surgical revascularization may be attainable early in life and should improve the long-term end result. Embolization of enormous collateral vessels or pneumonectomy may also be useful in the treatment of pulmonary artery hypertension. Hypertrophied bronchial arteries and aortopulmonary collateral vessels in unilateral absence of a pulmonary artery can lead to hemoptysis. Conventional angiography could also be carried out for recurrent or main hemoptysis to identify collateral vessels and for remedy with embolization. A thoracic aortogram will reveal the bronchial arterial anatomy and aortopulmonary collateral vessels. Selective catheterization and embolization of bronchial arteries or collateral vessels can then be carried out with a gelatinous sponge materials, which is reabsorbed with related rebleeding danger or with polyvinyl alcohol particles, a permanent embolization material. Medium-sized particles (300�500 microns) are most well-liked, as smaller particles can cause bronchial necrosis and cross through collaterals to the pulmonary veins, causing non-target embolization. Metal coils ought to be averted as a end result of they have an inclination to occlude proximal vessels and prevent repeat embolization.
Septra 480 mg for sale
Other laboratory assessments, corresponding to wound cultures, synovial fluid, peritoneal fluid, and try to increase cardiac output. Tachypnea could also be an indication of hypoxia or may represent respiratory compensation of a metabolic (lactic) acidosis. Because extreme sepsis is outlined by organ failure, look for proof of acute kidney injury, shock liver (elevated bilirubin), coagulopathy (elevated prothrombin time/ international normalized ratio/partial thromboplastin time), and thrombocytopenia. Pa0 2 measurement in contrast with Fi0 2 could also be useful in determining the presence of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Although arterial and venous samples are practically equivalent, lactate is ideally measured at the bedside. In the time it takes for blood to journey to the lab, blood cells bear anaerobic metabo lism, causing false elevations. Clearance of lactate (delta lactate) of 1 0% or larger indicates a significant reduction in mortality, whereas no change might signify a 60% mortality. These sufferers should have a central line and Foley catheter placed for monitoring. The goals of this method embrace optimizing preload, afterload, and central venous oxygen saturation (Scv0 2) in a stepwise strategy. Preload is addressed with fluid resuscitation in the type of 1,000 mL crystalloid boluses administered over 30 minutes and repeated as essential to obtain a central venous pressure of 8 - 1 2 mmHg. Once achieved, afterload is treated with vasopressors (norepi nephrine or dopamine) to elevate the imply arterial stress to sixty five mmHg. Scv0 2 is a measurement of oxygen saturation in blood returning to the superior vena cava. When low, either the physique is delivering insufficient oxygen or the tissues have to extract a big quantity to correct their oxygen debt. Oxygen delivery (D0 2) may be augmented by administering extra oxygen (maximize the pulse oximetry), rising oxygen carrying capability with blood transfusions to a hematocrit of 30%, and growing oxygen supply by "whipping" the heart with dobutarnine for higher inotropy. A decrease in post-treatment lactate by 10% has been proven to be equal to reaching a Scv0 2 70%, using the identical treatment algorithm. Lastly, source management involves removal of the nidus of infection when attainable (eg, elimination of contaminated central strains or drainage of abscesses). Imaging Chest radiographs are usually included for many septic sufferers when the presentation is concerning or the etiol ogy is unsure. Targeted imaging must be thought-about primarily based on clinical presentation (eg, computed tomography scan of the abdomen/pelvis within the febrile patient with stomach ache and up to date surgical procedure for Crohn disease to assess for potential abscess). Next, determine the sepsis severity through medical assess ment, point of care lactate, laboratory evaluation for end organ damage, and blood stress response to fluid resuscitation. Patients with uncomplicated sepsis should have investigation to determine the infectious supply and be handled with antimicrobials and fluids. Other patients could additionally be admitted to basic medical ground or step down, depending on the nursing ratios and capabilities of that specific unit. Sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock: Current evi dence for Emergency Department management. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International tips for administration of severe sepsis and septic shock. Lactate c learance vs cen tral venous oxygen saturation as targets of early sepsis therapy: A randomized medical trial. Duration of hypotension prior to initiation of effective antimicrobial remedy is the crucial determinant of survival in human septic shock. Viral pharyngitis, strep throat, and pyelonephritis are examples of infections that often could enable the affected person to be discharged to house. Fitch, M D Key Points � � the basic triad of meningitis consists of fever, neck stiff ness, and a ltered menta l standing. However, all three of these are present less than half of sufferers with bacterial meningitis. In the early levels of illn ess the analysis may be very difficult, and evalua tion is focused on identifying sufferers who require urgent diagnostic testing and treatment.

Generic 480mg septra free shipping
Although usually protected by the arm, axillary structures are susceptible when the arm is kidnapped. The "tickle" reflex causes us to recuperate the protected place rapidly when a risk is perceived. From the axilla, neurovascular constructions cross to and from the whole higher limb, together with the pectoral, scapular, and subscapular areas as well as the free higher limb. Axillary vein and artery: the axillary vein lies anterior and barely inferior to the axillary artery, each being sur- rounded by the fascial axillary sheath. For descriptive functions, the axillary artery and vein are assigned three parts positioned medial, posterior, and lateral to the pectoralis minor. In addition to transporting blood and lymph to and from the upper limb, the vascular structures of the axilla additionally serve the scapular and pectoral areas and lateral thoracic wall. Although their segmental identification is misplaced in forming the plexus, the original segmental distribution to skin (dermatomes) and muscles (myotomes) stays, exhibiting a cranial to caudal distribution for the pores and skin (see "Cutaneous Innervation of Upper Limb" on p. Two of the three cords give rise in flip to 5 nerves, and the third (lateral cord) provides rise to 3 nerves. In addition to the nerves arising from the cords, 10 more nerves arise from the various parts of the plexus. Most nerves arising from the plexus comprise fibers from two or more adjacent anterior rami. Two types of motion happen between the arm and forearm on the elbow joint: flexion�extension and pronation�supination. A distally positioned assistant to the triceps, the anconeus, additionally lies inside the posterior compartment (6. It must be famous, nevertheless, that the extensors of the elbow are particularly necessary for raising oneself out of a chair, and for wheelchair activity. In either case, a single biceps tendon forms distally and attaches primarily to the radius. When the elbow is prolonged, the biceps is a simple flexor of the forearm; nevertheless, as elbow flexion approaches 90� and more energy is needed in opposition to resistance, the biceps is capable of two highly effective movements, relying on the position of the forearm. When the elbow is flexed near 90� and the forearm is supinated, the biceps is most effective in producing flexion. The biceps barely operates as a flexor when the forearm is pronated, even in opposition to resistance. In this dissection of the best arm, the veins have been removed, apart from the proximal a half of the axillary vein. In this transverse section of the proper arm, the three heads of the triceps and the radial nerve and its companion vessels (in contact with the humerus) lie within the posterior compartment. The pectoralis major and minor muscular tissues are reflected superolaterally, and the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus are reflected superomedially. However, a triangular membranous band, the bicipital aponeurosis, runs from the biceps tendon across the cubital fossa, and merges with the antebrachial (deep) fascia covering the flexor muscle tissue in the medial facet of the forearm. To check the biceps brachii, the elbow joint is flexed in opposition to resistance when the forearm is supinated. When the forearm is extended slowly, the brachialis steadies the motion by slowly relaxing-that is, eccentric contraction (you use it to decide up and put down a teacup rigorously, for example). The brachialis all the time contracts when the elbow is flexed and is primarily responsible for sustaining the flexed position. To take a look at the brachialis, the forearm is semipronated and flexed in opposition to resistance. For instance, the musculocutaneous nerve pierces it, and the distal a half of its attachment signifies the situation of the nutrient foramen of the humerus. Because its long head crosses the glenohumeral joint, the triceps helps stabilize the adducted glenohumeral joint by serving as a shunt muscle, resisting inferior displacement of the pinnacle of the humerus. The lateral head is the strongest but is it recruited into activity primarily in opposition to resistance (Hamill and Knutzen, 2008). Just proximal to the distal attachment of the triceps is a friction-reducing subtendinous olecranon bursa, between the triceps tendon and the olecranon.

Order septra visa
Posteroanterior chest radiograph (A) and double-contrast upper gastrointestinal fluoroscopic image (B) demonstrate a right-sided aortic arch with an aberrant left subclavian artery. The left subclavian artery causes an impression (arrow) and narrowing of the esophagus. When detected, there ought to be careful evaluation of the aortic arch and nice vessels. Note the four nice vessel branches (A) and the left innominate artery (B, arrow) with a right aortic arch (C, D). Common Variants Right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery Right aortic arch with mirror-image branching Right aortic arch with isolated left subclavian artery Clinical Issues Cyanosis and other congenital anomalies counsel mirror-image branching right aortic arch. Workup of dysphasia in an infant ought to include the exclusion of an aberrant left subclavian artery sort of proper aortic arch. Diminished pulses within the left arm or a steal phenomenon could be seen in the uncommon case of isolated left subclavian artery. Key Points Two major variants of the best aortic arch are most typical: aberrant left subclavian artery and mirror-image branching patterns. Aberrant left subclavian artery is almost all the time an incidental discovering in an asymptomatic patient. Mirror-image branching is commonly related to cyanotic congenital coronary heart disease. Rings, slings, and other things: vascular compression of the infant trachea updated from the midcentury to the millennium-the legacy of Robert E. It represents 6�8% of all congenital coronary heart defects and is extra commonly present in males than in females, with a 2:1 ratio. Variant types can occur proximal to the left subclavian artery and infrequently within the belly aorta. Clinical Features Typically, the medical diagnosis is bimodal and differs in accordance with associated anomalies. Infantile presentation is normally congestive coronary heart failure and is often related to ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, and bicuspid aortic valve. Presentation in older youngsters and in adults is mostly associated with fewer anomalies and will present with hypertension or, less commonly, as an asymptomatic imaging discovering or ruptured intracranial aneurysm. In adults the most typical presenting signal is hypertension and, without therapy, the common age of survival is 35 years with a 75% mortality price by age forty six years. Physical examination findings include an elevated systolic blood pressure within the higher extremities in comparison to that in the decrease extremities. Less generally, in a variant of coartation that happens proximal to the left subclavian or to an aberrant proper subclavian artery, a distinction in blood stress can be found between the best and left arm. Other scientific findings embody diminished femoral pulses or decreased arterial pressures within the lower extremities. On auscultation, a cardiac systolic thrill because of left ventricular enlargement might be heard. Additionally, because of extensive collateral circulation to supply the descending aorta, a systolic murmur could be heard in the intercostal regions. This consists of collaterals between the interior mammillary and epigastric arteries and the parascapular and intercostal arteries. Also, girls with coarctation have a 4% likelihood of getting youngsters with the abnormality. Anatomy and Physiology Recent theories have advised that coarctation happens from elastic vascular wall defects somewhat than from a discount in intrauterine blood move. This is according to histological findings of medial necrosis observed How to Approach the Image Diagnosis may be made through multiple modalities. In addition, collateral circulate across the stenosis may produce bilateral notching of the posterior third of the third through eighth ribs on chest radiograph. Furthermore, in uncommon cases the location of the coarctation affects the sample of notching, since collateral blood circulate develops proximal to the coartation. A coarctation proximal to the left subclavian artery results in unilateral right-sided rib notching, whereas unilateral left-sided rib notching happens when a coarctation is present proximal to an anomalous right subclavian artery.


