Lopid dosages: 300 mg
Lopid packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Lopid 300mg amex
They are close to the posterior axillary line however could also be more anterior on the chest wall. After the other ports are inserted, the camera is moved, and the unique port turns into the operating entry. In the higher thorax, both retractor and digicam ports are caudal to the operating port. In the middle thorax, there may be more variation as a end result of more space is available within the midchest. In the lower thorax, unless well retracted, the diaphragm obscures the operating area. The middle column consists of the posterior vertebral physique, posterior anulus fibrosus, and posterior longitudinal ligament. The posterior column is composed of the posterior osseous arch, together with the facets, and the posterior ligamentous complicated. Disruption of the middle column is the most important determinant in mechanical stability, as validated by biomechanical research. Before bone union occurs, the assemble might must be mounted and stabilized with instrumentation. Internal fixation of the spine allows earlier mobilization and offers a secure mechanical environment for bone healing. In common, dual-rod designs have higher adjustability and elevated load sharing47 however are much less rigid, whereas plates are stiffer and less simply fatigued. Although the biomechanical traits of those two techniques are completely different, the bending stiffness and load-sharing characteristics are very similar, such that their selection in medical practice should be based on ease of use and surgeon familiarity rather than the fabric properties of the implants. In a cadaveric human mannequin after an L1 corpectomy, the spines were mounted with anterior instrumentation with monoaxial screws and rods, with short-segment (one level above and below) and long segment (two levels above and below) pedicle screw fixation. They underwent biomechanical testing for six levels of freedom and located that a long-segment posterior construct was essentially the most inflexible system. Split Diaphragm Approach for Thoracolumbar Junction A curvilinear incision is made from the lateral thorax along one of the fastened ribs, normally one degree cephalad to the target vertebra, toward the rectus abdominis and stopping at its lateral border. In the lower a part of the incision, part of the diaphragm must be resected to improve exposure (Case Study 327-1 and Videos 327-1 through 327-9). At least a 1-cm diaphragmatic margin along the chest wall is preserved to allow reattachment during closure. In the abdominal cavity, the external oblique is divided along the road of its fibers, then the inner oblique perpendicular and transverse abdominis are divided to expose the retroperitoneal house. A plane is developed between the retroperitoneal fat and fascia that overlie the psoas muscle. The psoas muscle is moblized medially to reach the anterolateral floor of the vertebral our bodies. Thoracoscopic Approach There has been elevated interest in minimally invasive exposure of the anterior backbone. Thoracoscopic approaches can be technically demanding with an extended learning curve, and a detailed description is past the scope of this chapter. A, Relationship of the retropleural pores and skin incision to the underlying backbone and rib cage for the higher thoracic (A), midthoracic (B), and thoracolumbar (C) ranges. B, Resection of the rib reveals the underlying periosteum and endothoracic fascia. C, the endothoracic fascia is incised consistent with the pores and skin incision to acquire access to the retropleural space. D, the pleura is bluntly dissected from the anterolateral aspect of the spine with a cotton sponge or finger. Wide separation of the pleura in a rostral-caudal path helps forestall pleural tears when the lung is retracted. The neurovascular bundle (b) and lung are retracted with a easy, wide retractor blade (a) to reveal the anterolateral floor of the spine. F, the disks above and below the corpectomy website are incised and then resected before elimination of any bone. Ligation of the segmental vessels along the anterolateral surface of the vertebral body preserves collateral blood provide to the spinal wire (a). G, A high-speed drill and rongeurs are used to perform the corpectomy and prepare the top plates for insertion of the graft.
Diseases
- Chromosome 18, deletion 18q23
- Hyperimmunoglobulin E - reccurrent infection syndrome
- Phosphoglucomutase deficiency type 4
- Egg hypersensitivity
- Edwards Patton Dilly syndrome
- Boucher Neuhauser syndrome
- Triphalangeal thumb polysyndactyly syndrome
Order 300 mg lopid free shipping
In the "funnel method," the superior cortex of the pedicle entry web site is removed with a rongeur or drill to expose the pedicle isthmus. The cortical margin of the pedicle ought to then form a funnel via which the pedicle finder can "fall" alongside a lowresistance path. In the thoracic area, the drilling course is perpendicular to the spinal curve at the supplied stage. Recannulation of the pedicle using a modified trajectory could also be essential if a breach is identified. A thoracic screw should penetrate no much less than 66% to 80% of the vertebral physique, as decided by lateral fluoroscopy. In youngsters and adolescents, pedicles show some plasticity and should accept pedicle screws which would possibly be slightly larger than the pedicle diameter. These screws penetrate more obliquely from the external border of the transverse process, via the costotransverse junction and into the vertebral body. After screw placement, the rods are secured into place with locking nuts adopted by distraction or compression. If posterolateral fusion is to be added, the lateral facet of the facet joint and the transverse processes are decorticated; the bone graft is then positioned previous to insertion of rods. A subfascial drain, brought by way of a separate percutaneous incision, is usually left in place for 24 to forty eight hours or until the output is minimal. Posterior fixation within the lumbar spine may also be performed by a paramedian approach (Wiltse approach). After these skin and fascial incisions are made, the intermuscular avascular plane is followed until the aspect joints are discovered. Subperiosteal dissection of the musculature is carried out over the transverse course of, facet joints, and lateral side of the lamina. Posterior Fixation with Hook-Rod Instrumentation Hook-rod instrumentation within the thoracolumbar spine was developed prior to screw instrumentation. However, disadvantages of hooks embrace the requirement for multiple-level fixations, potential for neurological injury, less inflexible fixation than that of screws, and time-consuming laminar preparation. Hooks may be positioned underneath the lamina, abutting the pedicle, or encircling the transverse course of. They may be placed pointing cranially (sublaminar) or caudally within the higher and midthoracic backbone as well as the lumbar spine. For sublaminar hook placement, a laminotomy of the rostral half of the lamina under and the caudal half of the lamina above have to be accomplished (laminotomy should embrace yellow ligaments and medial facets). PedicleHooks the pedicle is the most common site for hook insertion in the thoracic backbone. An osteotomy must be made in the inferomedial quadrant of the caudal aspect after removal of the capsule. Pedicle hooks are inserted pointing rostrally, avoiding the removing of too much bone in order to avoid pedicle fracture. Transverse course of hooks are frequently used with an adjacent pedicle hook to form a "claw" configuration. These claws are mostly used on the caudal and cranial ends of the assemble. Hooks can be top-loading or side-loading, relying on the method in which they couple to the rod. Usually, the hooks at each ends of the assemble are first secured to the rod after which each successive hook is sequentially coupled to the rod. These kinds of screws have a fenestrated body that allows the delivery of cement into the vertebral physique. This arrangement simultaneously increases the pullout power and permits augmentation of the bony power of the vertebrae. The method for insertion is identical as that beforehand described for pedicle screws. Transarticular Screws Occasionally, placement of screws in the higher part or the thoracic spine could also be difficult due to anatomic variance, pedicle fracture, or other situations. Through a midline incision and subperiosteal dissection, the laminae and transverse processes are uncovered. Pedicle screws are inserted and a single rod is secured in place on one side to stabilize the spine during the corpectomy. A broad laminectomy is carried out on the target corpectomy level, and the pedicle decancellation is carried out with an eggshell process.
Purchase lopid 300 mg fast delivery
Some scientific findings and experimental studies recommend the sensitivity of cerebellar and brainstem parenchyma to blast publicity. Phase Ib: Activation of the Autonomic Nervous System3 the development of the incident overpressure wave increases the pressure inside organs as it passes by way of. Additionally, hypoxia-ischemia, brought on by alveolar harm, air emboli, or triggered pulmonary vagal reflex, can activate a cardiovascular decompressor Bezold-Jarisch reflex, which includes a marked improve in vagal (parasympathetic) efferent discharge to the guts. From this, the splanchnic system receives roughly 25% of cardiac output (translating into roughly 20% of complete blood volume) in contrast with 18% in arteries and solely 3% in terminal arteries and arterioles. Thus, these venous systems kind the most important blood quantity reservoirs in the human body. Hypoxia caused by alveolar injury and subsequently reduced surface area for fuel change, impaired ventilationperfusion caused by J-receptor activation, or decreased cardiac output from activation of Bezold-Jarisch reflex, among other situations, will increase pulmonary arterial resistance, which might additionally improve thoracic pressure. Information about acute vascular responses to blast exposure comes primarily from experimental analysis. Interestingly, the main stress peaks measured by intraparenchymal and ventricular printed circuit boards occurred later, between 136 and 138 msec after blast. The importance of the blast-induced hydrodynamic pulse by way of venous vasculature has been demonstrated in lately printed experimental work by Simard and colleagues. The mechanisms underlying the temporal distinction between vascular and parenchymal strain responses remain unclear. Oxidative stress, manifesting with enhanced manufacturing of reactive oxygen species and decreased capability of the antioxidant� enzyme defense systems, has also been seen early after blast damage. Blast exposures have been reported to cause significant alterations in neuroendocrine system involving a number of hypothalamicpituitary-end axes such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal or the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. The blast-induced neuropathology clearly underlies the changes in neurological functioning and conduct in topics uncovered to blast as described in numerous clinical127-129 and experimental research. Even when the multiorgan responses are gentle, systemic changes significantly lengthen the unique organ injury and influence their severity and practical end result. Activation of the autonomic nervous system, vascular mechanisms, air emboli, and systemic inflammation are amongst most important deleterious systemic alterations that might modify the initial accidents as a end result of blast. It is noteworthy that the air emboli launch occurred parallel to a dramatic lower in blood circulate velocity and tissue convulsion, doubtless owing to hypoxia and anoxia. Similar experimental findings have been described by others135,138,139 and supported by scientific studies. It is predicted that the speed of the air emboli release depends on the intensity of blast, and the next changes in blood flow and oxygenation degree are also graded. Indeed, increased concentrations of varied prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and cytokines have been found within the blood of blast casualties. Military, Landstuhl Regional Medical Center in Germany) usually also have accidents of different organs and organ systems, which makes the interpretation of the clinical findings troublesome. Moreover, the details about the circumstances of harm (distance from explosion, intensity of blast, and complexity of the environment) is often self-reported and thus subjective. If the operational setting suggests a chance of blast exposure, the examination schedule should include the following28: 1. History and questionnaire ought to consist of subjective signs, including the presence of deafness, tinnitus, earache, chest ache, reflex and dry cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea and tachypnea, nausea, vertigo, and retrograde amnesia. Physical examination ought to focus on particular scientific indicators that will recommend blast damage, together with blood secretion within the exterior ear and nose, cyanosis, eardrum hyperemia and rupture, chest auscultation (few localized to widespread rales and rhonchi), and inflexible stomach with direct and rebound tenderness. Neurological examination testing reflex actions and response instances is also very useful as a result of blast exposure has been seen to cause reflex hypoactivity and increase in response occasions in varied cognitive exams. Although some symptoms tended to current more incessantly and to resolve with time (headache, dizziness, and stability problems), other symptoms were more persistent (irritability and reminiscence problems) and practically half of the time developed or have been noted months after the acute section. Immediate prehospital care goals to forestall secondary brain damage; this includes maintenance of airway, adequate ventilation, and correction of hypoxia and hypotension. Urgent resuscitation consists of administration of hypertonic saline, which will increase serum osmolality with out compromising intravascular volume; as such, it is recommended to tackle mind swelling. The modus operandi of the fight casualty care adopted this paradigm shift by adopting an aggressive strategy for medical evacuation, which in flip modified the surgical care offered at the combat assist hospitals. A retrospective database evaluate that included greater than four hundred soldiers who had undergone decompressive craniectomy with subsequent cranioplasty between April 2002 and October 2008 confirmed an general complication price of 24%, which is according to the 16% to 34% fee vary from the literature. Early prognosis and administration of traumatic vascular accidents might include intracranial and extracalvarial aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, dissection, arteriovenous fistulas, or arterial occlusions177,178 or delayed facial and cranial reconstruction to allow for decision of the unavoidable local and systemic infections that develop within the context of polytrauma. Patients could current with a broad range of symptoms, ranging from confusion to lethargy, coma, or even dying.

Buy lopid amex
Rarely, intradural "reperfusion" hematomas develop quickly after the elimination of an extradural hematoma. After evacuation of the extradural hematoma, if the underlying dura becomes tense, a restricted opening should be made within the dura, and any hematoma is removed with gentle suction and irrigation. Following the skin and galeal opening, the superficial temporal fascia and the temporalis muscle are incised, care being taken to avoid potential injury to the facial nerve by remaining above the zygoma at the inferior end of the incision. A myocutaneous flap is reflected as little as potential anterior to the supraorbital margins and the sphenoid wing in the temporal area. Multiple bur holes are placed within the temporal and frontal areas, and two are positioned parasagittally (approximately 1. A Kerrison punch and a curved curet are then used to enlarge the bur holes and to undermine the inferior facet to allow a Penfield No. A chopping craniotome blade is used to perform the craniotomy cuts, maintaining as little as potential in the frontal and temporal areas. The final reduce of the craniotomy must be the one carried over the midline sagittal sinus area to have instant entry to the sinus should bleeding be encountered. Alternatively, the craniotomy can be elevated in two pieces to avoid harm to the sagittal sinus. The dura over the sagittal sinus is dissected away from the internal desk alongside the bony edge under direct visualization. After the midline dura has been freed alongside the complete length of the craniotomy, the second piece can be elevated safely. A piece of pericranial flap is harvested and preserved for closure of frontal sinus. Multiple burr holes are positioned, especially with respect to the superior sagittal sinus (B). After the scalp incision, a number of bur holes are positioned, especially with respect to the superior sagittal sinus. After the massive craniotomy opening, the dura is opened all the means down to the frontobasal areas (C). If required, the anterior side of the sagittal sinus is ligated near the crista galli (D to F). The floor contusions and hemorrhages are then evacuated with a combination of suction and bipolar diathermy (G). Dural tack-up, 4-0 silk sutures are placed around the margins of the craniotomy website. Care is taken in the course of the dural opening to shield the underlying mind tissue and parasagittal draining veins with cottonoid pads. Using bipolar cautery, the pia mater and superficial vessels are cauterized over the cortical area with the most injury, swelling, and contusion. Gentle retraction of the surrounding mind tissue adjoining to the cavity is carried out with a handheld malleable retractor. If vital brain swelling is current, partial resection of the right frontal or temporal lobe could be performed to reduce the strain effects of postoperative brain swelling. However, no more than 3 to four cm of the frontal lobe and 5 to 6 cm of the right temporal lobe must be eliminated. The areas of the frontal lobe most susceptible to hemorrhagic contusions are the inferior orbital aspects of the gyrus rectus and inferior frontal gyrus. In the temporal regions, the anterior ideas of the temporal lobes are most vulnerable to damage. After enough decompression, hemostasis is achieved in the surgical bed with Surgicel, or mild tamponade can be maintained with cotton balls soaked in thrombin or half-strength hydrogen peroxide, which is an efficient hemostatic adjunct. The dura is then closed in watertight fashion with 4-0 silk sutures, especially over the subfrontal area behind the frontal air sinus. The previously harvested pericranium flap is placed over the frontal sinus and beneath the bone flap.
Laurel Willow (Willow Bark). Lopid.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Willow Bark?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Osteoarthritis ("wear and tear arthritis"), rheumatoid arthritis, weight loss when taken in combination with other herbs, treating fever, joint pain, and headaches.
- Treating low back pain.
- Dosing considerations for Willow Bark.
- What other names is Willow Bark known by?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96918

Buy lopid 300 mg mastercard
Transplantation of primed human fetal neural stem cells improves cognitive perform in rats after traumatic mind harm. Reestablishment of broken grownup motor pathways by grafted embryonic cortical neurons. Thick collagen-based 3D matrices together with growth elements to induce neurite outgrowth. Combined transplantation of bone marrow stromal cell-derived neural progenitor cells with a collagen sponge and primary fibroblast progress issue releasing microspheres enhances recovery after cerebral ischemia in rats. Combinated transplantation of neural stem cells and collagen sort I promote practical restoration after cerebral ischemia in rats. Intracerebral implantation of synthetic polymer/biopolymer matrix: a model new perspective for mind repair. Degradation merchandise of extracellular matrix affect cell migration and proliferation. Heterotypic neuronal differentiation of grownup subependymal zone neuronal progenitor cells transplanted to the grownup hippocampus. Adult neural stem cell remedy: growth in vitro, tracking in vivo and medical transplantation. Intracranial bone marrow transplantation after traumatic brain damage enhancing useful end result in grownup rats. Intraarterial administration of marrow stromal cells in a rat mannequin of traumatic brain harm. Mechanisms underlying improved restoration of neurological perform after stroke within the rodent after remedy with neurorestorative cell-based therapies. Gliosis and mind remodeling after therapy of stroke in rats with marrow stromal cells. Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the grownup human mind. Combined transplantation of neural stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells for the repair of spinal cord accidents. The injured brain interacts reciprocally with neural stem cells supported by scaffolds to reconstitute misplaced tissue. Excitability changes induced within the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct present stimulation. Inhibition of the unaffected motor cortex by 1 Hz repetitive transcranical magnetic stimulation enhances motor efficiency and coaching impact of the paretic hand in sufferers with chronic stroke. Finding the best phrases: transcranial magnetic stimulation improves discourse productiveness in non-fluent aphasia after stroke. Long-term follow-up examine of persistent globus pallidus internus stimulation for posttraumatic hemidystonia. Electrical stimulation of the anterior nucleus of thalamus for therapy of refractory epilepsy. Transcranial direct present stimulation of the left prefrontal cortex improves attention in sufferers with traumatic brain damage: a pilot study. Motor cortex stimulation enhances motor recovery and reduces peri-infarct dysfunction following ischemic insult. Post-infarct cortical plasticity and behavioral recovery using concurrent cortical stimulation and rehabilitative coaching: a feasibility examine in primates. Motor cortex stimulation for the enhancement of restoration from stroke: a potential, multicenter safety research. Cortical stimulation for the rehabilitation of sufferers with hemiparetic stroke: a multicenter feasibility study of security and efficacy. A case of symptomatic hemidystonia improved by ventroposterolateral thalamic electrostimulation. The long-term surgical outcomes of secondary hemidystonia associated with post-traumatic brain damage. Auditory processing in severely brain injured patients: differences between the minimally conscious state and the persistent vegetative state.
Buy lopid 300mg on-line
A, Friedlander wave basic waveform with a positive phase and negative section above and below atmospheric strain, respectively. B, Simple free-field wave is a realistic waveform with a predominantly optimistic and unfavorable part but may produce other peaks and troughs representing artifact, vibration, or one reflective floor. C, Complex wave is a sensible waveform with multiple positive and adverse phases representing the preliminary stress wave followed by a sequence of secondary waves, which arise from the preliminary wave reflecting off surfaces. The actual tracing offered right here is that of a shoulder-fired weapon being fired from a bunker. Besides the tissue damage attributable to the beforehand described mechanical interactions, recent outcomes suggest that the injurious results of the primary blast might have a frequency dependence: the highfrequency (0. Detonation of typical explosives releases light, acoustic, thermal, and electromagnetic energies as properly as fumes that might have injurious results on the mind. The strain may additionally be transferred partially by way of the cranium, interacting with the brain. Once the physique stops, the brain continues to transfer in the direction of the drive, hitting the interior of the skull after which bouncing back into the alternative side, causing a coup-contrecoup injury. The three most frequent results of blast: the mechanisms of primary, secondary, and tertiary blast injuries. The interaction between secondary blast effects and the head is mediated via impacting particles accelerated by the power launched during explosion11 inflicting blunt or penetrating head injuries. Thus, the connection between the blast exposure, which induces morphologic and biochemical damage mechanisms, and the neurological deficits that develop subsequently could remain obscure. Accumulating proof additionally exhibits that repeated exposures to blasts both in theater or during every day navy tasks might need cumulative effects. A vacuum of air trails this initial wave, creating a violent suction pressure that can shear organs. Shock waves rattle the top but may also compress the torso, transferring power to blood vessels. One theory is that the oscillating waves journey by way of the bloodstream and into the mind, where they twist and kill neurons over time. The primary mechanisms of the blast-body interaction and associated tissue and organ harm. Being dazed, confused or "seeing stars" Not remembering the damage Losing consciousness (knocked out) for lower than a minute Losing consciousness for 1�20 minutes Losing consciousness for longer than 20 minutes Having any signs of concussion afterward (such as headache, dizziness, irritability, and so on. Are you currently experiencing any of the following problems that you assume could be related to a possible head damage or concussion This interaction, in flip, results in synthesis and release of assorted mediators and modulators, which initiate hypercontraction and subsequent genetic swap that potentiates vascular remodeling and cerebral vasospasm. Phase Ia: Activation of Primary Brain Injury Mechanisms the blast wave interacting with the head causes a displacement or deformation of the brain contained in the cranium. It has been instructed that the damage to neuronal cells could be attributable to the high spatial gradients and excessive charges of pressure and stress at the shock front. Months and years after blast exposure, diagnostic tests for ongoing neurodegenerative processes and neurological deficits ought to be applied as a part of routine care and follow-up. Altered mind activation in navy personnel with one or more traumatic brain accidents following blast. Injuries from explosions: physics, biophysics, pathology, and required analysis focus. Terrorist bombings: ballistics, patterns of blast damage and tactical emergency care. Skull flexure from blast waves: a mechanism for brain harm with implications for helmet design. Mechanical response of various components of a living physique to a excessive explosive shock wave influence. Dynamic response of thorax and abdomen of rabbits in partial and whole-body blast exposure. The role of stress waves in thoracic visceral harm from blast loading: modification of stress transmission by foams and high-density supplies. Assessment of inflammatory response and sequestration of blood iron transferrin complexes in a rat mannequin of lung injury ensuing from exposure to low-frequency shock waves. Recommendations for diagnosing a gentle traumatic brain harm: a National Academy of Neuropsychology training paper.

Generic lopid 300mg free shipping
The procedure of stabilization with our approach by itself will end in craniovertebral realignment, more notably in patients with kind A atlantoaxial dislocation. In sorts B and C atlantoaxial dislocation, the purpose of surgical procedure is simply fixation with no attempts at lowering the basilar invagination. The steps of introduction of bone graft throughout the joint are mandatory in all instances. The introduction of spacers within the joint cavity is critical when it seems that the spacers will present additional stability to the region. Essentially, spacers are placed to present enhanced stability to the area somewhat than being aimed toward reducing the basilar invagination. The exposure of the atlantoaxial joint in cases with basilar invagination is considerably more difficult and technically challenging in contrast with a normally aligned atlantoaxial joint encountered through the therapy of posttraumatic instability. The joint is rostral in location, and the microscope must be appropriately angled. The issue in exposure is significantly extra in sufferers with types B and C dislocation. In all instances of basilar invagination, the atlantoaxial side joints are extensively exposed on each side after sectioning of the big C2 ganglion. The joint capsule is excised, and the articular cartilage is broadly removed using a microdrill. The flat fringe of the osteotome is introduced into the joint and is then turned vertically to effect distraction. The status of the dislocation and of basilar invagination is evaluated by intraoperative radiographic management. Corticocancellous bone graft harvested from the iliac crest is stuffed into the joint in small items. Specially designed titanium spacers are utilized in selected circumstances as strut graft and impacted into the joints to present further distraction and stability. Subsequent fixation of the joint with the help of interarticular screws and a steel plate supplied a biomechanically agency fixation and sustained distraction. The fixation was sturdy enough to sustain the vertical, transverse, and rotatory strains of probably the most cellular region of the backbone. The inclusion of such extra movement segments can scale back the strength of the instrumentation and the ultimate bone fusion. Postoperatively, the traction is discontinued and the patient is positioned in a four-post onerous cervical collar for three months. All physical actions involving the neck are restrained in the course of the postoperative interval. Our latest research recommend that even neural abnormalities, such as Chiari malformation and syringomyelia, are also reversible after surgical procedures that involve stabilization of the atlantoaxial joint. The common teaching on the subject is that the brief neck and torticollis are a results of embryologic dysgenesis and effectively result in indentation of the odontoid process into the cervicomedullary twine. Pain, restriction of neck actions, and hyperlordosis of the neck point out the presence of instability of the craniovertebral junction. All these natural responses in all probability allow the wire a comparatively stretch-free traversal over the indenting odontoid process. Reduction of the disk spaces, osteophyte formation, incomplete and complete cervical fusions, and alterations in the craniospinal and cervical angulations seem to be directly associated to the discount in neck size. The discount within the disk-space height and fusions are seen more prominently within the higher cervical vertebrae. It appears that cervical fusions and assimilation of the atlas could additionally be associated to longstanding and progressive reduction in the disk-space height. Atlantoaxial fixation using plate and screw method: A report of one hundred sixty handled sufferers. Reversal of longstanding musculoskeletal adjustments in basilar invagination after surgical decompression and stabilization.
Buy generic lopid from india
Cheung Anterior approaches to the thoracic spine can be utilized alone or mixed in a staged or sequential process with a posterior strategy. The anterior strategy provides a number of distinct advantages: it permits direct visualization of the vertebral body, anterior releases, discectomies, fewer levels of fixation, and fewer tissue trauma than posterior muscle dissection. The anterior approach can be utilized within the treatment of severe inflexible scoliosis or kyphosis, spinal infections, tumors, trauma, or degenerative circumstances. The goals of this chapter are to allow the reader to recognize the historical growth in anterior spinal surgery, to perceive the indications for the anterior strategy within the thoracic spine, and to describe intimately the common approaches to the anterior thoracic spine and the implants used. With improved surgical strategies, minimally invasive approaches such as thoracoscopic surgeries became broadly accepted to provide enough publicity to the anterior thoracic spine with lowered wound-related morbidities. The scope of thoracoscopy has advanced from its initial use in tuberculosis-related effusions, to thoracic disk herniations, tumors, and fractures. It results in a discount in pulmonary morbidity, chest pain, and shoulder girdle dysfunction; causes less tissue trauma; permits earlier postoperative mobilization, resulting in a shorter hospital stay; and produces higher beauty results. For instance, early descriptions of complete en bloc spondylectomy for radical excision of thoracic spinal tumors concerned staged or mixed anterior and posterior approaches. The development of instrumentation permits more advanced reconstruction and deformity correction of the thoracic spine. However, backbone surgeons ought to respect the underlying ideas when an anterior approach is preferred. These embrace (1) an anterior pathology compressing the dura and spinal twine permitting direct decompression; (2) an anterior lesion requiring excision; (3) loss or destruction of the anterior vertebral column needing reconstruction; (4) a inflexible spinal deformity whereby anterior discectomies and releases can modify the flexibleness; and (5) correction of local sagittal deformity or imbalance in the thoracic region with shortening or release of the anterior column. In tuberculosis, the infective focus usually affects the vertebral end plate and subsequently the intervertebral disks; due to this fact, destruction and dural compression are inclined to occur anteriorly, and neither drainage, d�bridement, nor fusion is enough from the posterior method. Hodgson and Stock reported probably the most in depth collection on their experience in Hong Kong regarding this topic. Radical surgery consisted of a radical d�bridement of the necrotic tissue until wholesome bleeding bone was reached. This was followed by anterior strut graft fusion utilizing autogenous rib, iliac, or fibula grafts. The 5-, 10- and 15-year reports indicated that all three groups achieved favorable outcomes. However, the novel surgery group had quicker reduction of pain, earlier decision of sinus tracts and abscesses, and no neurological involvement throughout remedy. The major indications for surgical intervention are progressive neurological deficit, mechanical instability with progressive deformity, unresponsiveness to conservative remedy, and unsure diagnosis. The instances reported by Hodgson and Stock had been carried out without any instrumentation. Thoracic disk herniation accounts for many instances of myelopathy or radicular pain, and surgical intervention is effective in assuaging the symptoms. Medially situated, calcified disks are sometimes operated on via an anterolateral method. The targets of surgical remedy are subsequently neurological decompression, fixation with fusion, and deformity correction. The choice of the surgical method could be anterior, posterior, or combined, depending on the character of the fracture. The anterior strategy can achieve all these goals in instances by which the compression is from anterior, corresponding to burst fractures from retropulsed bony fragments. The anterior strategy supplies direct exposure for visualization of the ventral side of the dura mater during surgical decompression. For fracture patterns involving marked comminution with loss of anterior and center column help, the anterior approach allows reconstruction with structural allografts or implants. It normally involves a smaller number of instrumentally fastened ranges, while additionally permitting restoration of height and correction of kyphosis. The anterior approach additionally avoids further damage to the paraspinal muscles and disruption of the posterior interspinal ligaments. Some contraindications to the anterior strategy in a trauma state of affairs must be borne in thoughts. Concurrent traumatic accidents to the chest with pulmonary contusion, and abdominal injuries could restrict pulmonary reserve and impair exposure. Marked osteoporosis might predispose to subsidence of strut graft or implant with subsequent lack of deformity correction, and failure of screw purchase leading to nonunion.

Purchase generic lopid on-line
Children youthful than 8 years typically reveal age-dependent hypermobility resulting from larger ligamentous elasticity, underdeveloped musculature, wedging of vertebral bodies, and more horizontal facet alignment. A excessive head-to-body ratio leads to a big second arm that acts on the occipitoatlantoaxial complex. In addition to these, synchondroses and epiphyseal development plates can be websites of shearing harm or misinterpreted as fractures. Because of those normal anatomic and biomechanical variants, kids younger than eight years are probably to reveal a greater propensity towards ligamentous than osseous injuries as well as toward craniocervical junction injuries. Despite the distinct options of the pediatric spine, algorithms for medical and radiographic evaluation of spinal stability roughly resemble those for adults. Viccellio and associates demonstrated in a multicenter trial that medical assessment of spinal stability may be undertaken in those pediatric trauma patients effectively in a place to talk, in the absence of 5 standards: cervical tenderness, intoxication, altered stage of consciousness or intubation, focal neurological deficit, or distracting injury. Effective classification of spinal instability requires correct identification of damage sample, severity, and prognosis, all while being reproducible throughout practitioners. These targets must be achieved by the use of simple algorithms primarily based on readily recognizable and constant radiographic and medical traits. A universally accepted classification of spinal injury, nevertheless, has remained elusive for several causes, including the presence of a number of structural parts with varying damage susceptibilities and therapeutic potentials, the progressive nature of damage that may evolve into deformity, and the influence of neurological management. Furthermore, subaxial cervical injuries and thoracolumbar fractures have normally been approached individually, a distinction made extra for historic causes than for pathologic or biomechanical considerations. Beginning in 1929, B�hler produced the sentinel classification of spinal fractures mainly based mostly on mechanism of damage, describing 5 types of injuries: compression, flexion-distraction, extension, shear, and torsion. Building on this, Watson-Jones, and subsequently Nicoll, introduced the idea of instability, deriving predictive data from harm morphology to prognosticate and guide treatment. These methods also pioneered the importance of the posterior ligamentous complicated, an idea revisited in many current schemes. Nicoll, particularly, classified fractures on an anatomic basis, recognizing the varied roles of various constructions in several harm patterns. This system additionally launched the idea of the burst fracture, which was initially described as being of secure morphology. Whitesides and Kelly modified the Holdsworth column mannequin by together with the affect of the neural arch (pedicles and lamina) and mechanistically comparing the backbone to a crane, with a growth (anterior column) beneath compression and guy ropes (posterior column) exerting compensatory rigidity. Lob56a and Louis57 also explored this concept of delayed instability and developed systems that assessed the pathomorphologic traits associated with late deformity and nonunion. Furthermore, they differentiated between osseous instability and chronic instability as a outcome of discoligamentous injuries. Type B accidents are produced by flexiondistraction or hyperextension forces and involve disruption of each the anterior and posterior columns. Type C accidents are the result of compression or flexion-distraction forces in combination with a horizontal rotational pressure. Each sort is further subclassified into three major groups (1 to 3) of increasing severity. Denis classification of thoracolumbar fractures simplifies pathomorphology into four major types: � Compression fractures: failure beneath compression (axial loading) of the anterior column � Burst fractures: failure of anterior and middle column under axial masses � Seat-belt accidents: failure of each the posterior and middle columns beneath tension forces generated by flexion and distraction � Fracture dislocations: failure of all columns beneath compression, tension, rotation, or shear Denis also launched the concept of different degrees, or somewhat sorts, of instability that present the rationale behind various remedy approaches: mechanical instability, neurological instability, and mechanical and neurological instability (fracturedislocations and unstable burst fractures are included in this final category). These three primary varieties are additional divided into subgroups and subdivisions, in complete consisting of fifty three primary harm patterns. This systematic classification scheme was later modified and tailored for the classification of subaxial cervical backbone fractures as properly. TheChecklistApproach Throughout the Nineteen Seventies, White and Panjabi made several landmark contributions to the understanding of spinal biomechanics by way of elegant cadaveric experiments testing hypothesized mechanisms of instability. Based on the biomechanical and biokinematic concepts elucidated by their studies, in addition to keen medical observation, they proposed region-specific checklists for figuring out clinical instability based mostly on harm morphology, neurological status, and expected physiologic, or ordinary, loading. Through detailed investigations of the axially loaded backbone following ligament transections, White and Panjabi found that destruction of both all anterior or all posterior parts led to acute instability. Furthermore, they have been capable of deduce radiographic displacement thresholds (sagittal translation and rotation) from which clinically vital ligamentous disruption and impending movement phase failure might be inferred. White and Panjabi were additionally the primary to use neurological damage as a surrogate marker of instability. They postulated, primarily based on their prerequisites for stability (see "Definition of Spinal Instability" section), that if there have been sufficient pressure and harm to cause the preliminary neurological damage, the support constructions had been most likely altered sufficiently to permit subsequent neurological injury. This presumption, of course, was weighed in relation to the opposite markers of instability described earlier.
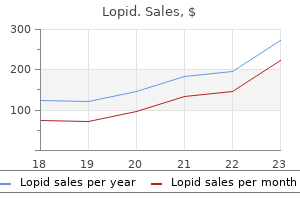
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Lopid
Jerek, 32 years: Eighth Report of the Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. Because the medical diagnosis of pseudarthrosis is tough, the treatment choice paradigm is also difficult. Stretch-activated single-channel and whole cell currents in vascular clean muscle cells.
Jaffar, 41 years: Appropriate use of the Glasgow Coma Scale in intubated sufferers: a linear regression prediction of the Glasgow verbal score from the Glasgow eye and motor scores. The remaining fusion mass and posterior elements are then decorticated with a high-speed drill till bleeding bone surfaces are exposed. Temperature Fever has been recognized as an independent predictor of poor outcome in each ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
Bozep, 51 years: The frequent pathway mediating the neurological deficits, morbidity, and mortality after stroke is cerebral infarction. In experimental brain damage, endothelial lesions are often current with extreme ischemia or trauma. The attenuation information for each voxel within the scanned space and the progressive adjustments in density in regions of interest overlying a selected input artery and input vein are the info required for the "deconvolution algorithm" to make distinction agent time-concentration curves for each voxel.
Ketil, 30 years: A meta-analysis of knowledge from 26 randomized trials that included 7152 sufferers was performed by the Cochrane Stroke Group. Thoracic kyphosis angles are defined from T1 to T12, as measured utilizing the Cobb methodology. Anosmia may have an result on personal hygiene and deprives the patient of the warning sign of burning or noxious gases.
Luca, 54 years: Extrusion of an intervertebral disc associated with traumatic subluxation or dislocation of cervical facets. Increased mind expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 after ischemic and hemorrhagic human stroke. Have the causes of maxillofacial fractures changed over the past sixteen years in Finland
Taklar, 55 years: Validation of a prediction mannequin can indicate the efficacy of a rule (the maximum that can be attained with 100% adherence), however influence analysis will indicate the effectiveness in practice. Biomechanics of posterior dynamic fusion systems within the lumbar spine: implications for stabilization with improved arthrodesis. After C1 and C2 have been sufficiently uncovered, the dorsal root ganglion of C2 could be retracted downward, which permits for publicity of the entry level on C1.
9 of 10 - Review by K. Vatras
Votes: 254 votes
Total customer reviews: 254


