Terazosin dosages: 5 mg, 2 mg, 1 mg
Terazosin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Generic terazosin 2 mg online
This is a rare congenital syndrome characterized by a defect in small- and large-bowel chloride absorption that results in a persistent diarrhea with excessive chloride losses within the stool. The alkalosis is sustained because of hypochloremia, hypokalemia, and volume contraction with resultant secondary hyperaldosteronism. The metabolic derangements caused by loop diuretics are equivalent to these seen in Bartter syndrome. Chronic hypercapnia, as seen in bronchopulmonary dysplasia or cystic fibrosis, results in an elevated serum bicarbonate concentration from metabolic compensation. Affected patients have chloride depletion, which may be worsened by concomitant diuretic use. With resolution of the hypercapnia, the bicarbonate concentration remains excessive till the chloride depletion is corrected. Urinary Chloride Level Higher Than 20 mEq/L with Hypertension Pediatric patients with hypertension either have elevated ranges of aldosterone or act as in the occasion that they do. Increased aldosterone "results" trigger renal retention of sodium, which ends up in elevated blood pressure. The disorders of mineralocorticoid extra are characterized by volume enlargement and hypertension (see Table 46. The mineralocorticoid extra stimulates the renal excretion of H+ and K+, resulting in metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia. The numerous causes may be differentiated by evaluating the renin-aldosterone axis. Treatment is geared toward eradicating or correcting the supply of the mineralocorticoid excess. Urinary Chloride Level Higher Than 20 mEq/L with Normal Blood Pressure Bartter syndrome and Gitelman syndrome. These unusual autosomal recessive problems end result from defects in varied ion transporters inside the nephron. Affected patients current with a historical past of failure to thrive, polyuria, polydipsia, and a bent for dehydration. Children with Gitelman syndrome, however, are more susceptible to febrile seizures and tetanic episodes (Table forty six. Treatment of Metabolic Alkalosis Treatment focuses on correcting the underlying disorder and is dependent upon the pathophysiologic mechanisms of the alkalosis. Patients with a chloride-responsive metabolic alkalosis (urine Cl- <15 mEq/L) respond to volume repletion; both sodium and potassium chloride are necessary. In uncommon instances, if alkalosis persists regardless of chloride supplementation, the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor acetazolamide can be utilized to enhance urinary bicarbonate losses. In patients present process persistent gastric drainage, administration of both an H2 blocker or H+ pump inhibitor could be useful by decreasing the gastric H+ secretion. The degree of hypercarbia drives the signs in a affected person with respiratory acidosis. Patients with acute respiratory acidosis have extra signs than sufferers with persistent respiratory acidosis. The management of respiratory acidosis is directed toward improving alveolar ventilation and treating the underlying dysfunction. In a spontaneously respiration child, this could result from fever, sepsis, delicate bronchial asthma, panic attack, or central nervous system disorders. In the intensive care unit, the commonest trigger is mechanical overventilation of an intubated baby. A metabolic response to an acute respiratory alkalosis is mediated by hydrogen ion release from nonbicarbonate buffers and happens within minutes. Metabolic compensation for a respiratory alkalosis develops steadily and takes 2-3 days. Chronic respiratory alkalosis is the only acid�base dysfunction during which the pH may be completely normalized by the compensatory mechanisms. Symptoms of acute respiratory alkalosis could additionally be chest tightness, palpitations, lightheadedness, circumoral numbness, or extremity paresthesias. Respiratory acidosis may finish up from both pulmonary illness, such as in severe bronchiolitis, or nonpulmonary disease, similar to a narcotic overdose. The parethesias, tetany, and seizures are thought to be related to the lower in ionized calcium that occurs because alkalemia causes more calcium to bind to albumin. The deviations in pH are more marked when 2 primary occasions block the compensation of one another, such as the mixture of a metabolic acidosis and a respiratory acidosis seen in a patient with shock and respiratory failure.
Diseases
- Koilonychia
- Craniosynostosis alopecia brain defect
- Hereditary coproporphyria
- Oral leukoplakia
- Methylcobalamin deficiency cbl G type
- Costello syndrome
- Pilotto syndrome
- Fukuyama-type muscular dystrophy
- Pheochromocytoma as part of NF
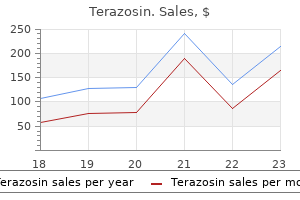
Discount terazosin 2 mg fast delivery
Serologic techniques are probably helpful in establishing a prognosis of a selected infection by demonstrating a 4-fold rise in titer between samples obtained in the course of the acute and convalescent phases of illness. Histopathology Punch biopsy for gentle and electron microscopy and immunohistologic research should be thought-about for diagnostic functions for patients presenting with fever and bullous lesions which would possibly be clearly not typical pyodermas; fever and nodular lesions; or lesions suggestive of vasculitis (palpable purpura, livedo reticularis). A punch biopsy with indirect immunofluorescent antibody staining may also be useful for sufferers with petechial lesions, particularly in an acral distribution, for the early prognosis (at days 4-8 of illness) of an infection with R. The low sensitivity of the take a look at could also be associated to the rickettsiostatic effect of antimicrobial therapy earlier than presentation, nevertheless it indicates clearly that decision making within the acute care setting is restricted by the excessive fee of false-negative classifications anticipated with this process. Diagnosis and Decision Making Accurate diagnosis is dependent upon cautious synthesis of selected information obtained from the scientific evaluation. Because most children with acute episodes of fever and rash have a standard, self-limited infectious disease, a selected prognosis can often be established simply by sample recognition alone. Because the spectrum of infectious pathogens is broad, and the presenting complaints or features of the rash could also be atypical, and every so often, the diagnosis might not yield simply to easy sample recognition. In these conditions, empirical use of the laboratory may show helpful to the clinician. This technique was based mostly on physician data of the age-specific and/or seasonal incidence of infectious pathogens in the population studied. It may be preferable to "watchful waiting" and serial medical follow-up when the patient is judged to be at risk for a treatable sickness associated with significant subsequent morbidity. Well-appearing patients with fever and petechial rash current a problem to the clinician. Such patients with cough or emesis and petechiae solely above the nipple line, and a optimistic streptococcal antigen test, or sufferers with normal leukocyte, absolute neutrophil, and platelet counts and a standard prothrombin time are exceedingly unlikely to have an invasive bacterial illness corresponding to meningococcemia. The subset of patients with fever and rash who seem toxic, have unstable vital indicators, or altered psychological status should have a comprehensive evaluation and a prognosis confirmed as shortly as attainable to detect potentially life-threatening underlying infection. The majority (75-85%) of affected youngsters are lower than 5 years old, and infants aged <6 months and kids over 5 years old are on the highest risk for coronary artery aneurysms. It is usually morbilliform, however may also be erythema multiforme-like (fixed erythematous goal lesions [see. Early prognosis is crucial to lower the risk of coronary artery aneurysms, which decreases to less than 5% in promptly handled sufferers. The syndrome is defined by fever, diffuse macular erythroderma with convalescent desquamation, hypotension, mucositis, strawberry tongue, and multiorgan dysfunction. Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Laboratory criteria for diagnosis include adverse results on the following exams, if obtained: blood or cerebrospinal fluid cultures (blood tradition could additionally be constructive for S. A possible case meets the laboratory criteria and 4 of 5 clinical standards and a confirmed case meets the laboratory and all 5 clinical criteria: Fever: temperature higher than or equal to 102�F (greater than or equal to 38. Muscular: severe myalgia or creatine phosphokinase stage no much less than twice the higher limit of regular 3. Renal: blood urea nitrogen or creatinine at least twice the upper restrict of normal for laboratory or urinary sediment with pyuria (greater than or equal to 5 leukocytes/high-power field) within the absence of urinary tract an infection 5. Hepatic: total bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase enzyme, or aspartate aminotransferase enzyme ranges no less than twice the higher limit of regular for laboratory 6. Central nervous system: disorientation or alterations in consciousness without focal neurologic signs when fever and hypotension are absent Clinical Syndromes In certain situations, the diagnostic strategy to disorders manifesting with fever and rash is wholly depending on an aggregation of nonspecific signs, symptoms, and laboratory results. These problems either have many underlying causes manifesting with overlapping features or have unknown causes for which no confirmatory exams have but been devised. These diseases are identified by recognizing patterns and sometimes by excluding different diagnoses; some are primarily based on formalized aggregation, termed syndromic analysis. Although syndromic diagnosis is based on specific medical criteria, some of the clusters of indicators, symptoms, and laboratory findings have been established initially for epidemiologic purposes (case definition) to facilitate exploration of an underlying cause. A genetic role is suspected given the 10- to 20-fold elevated incidence in Japan as in comparison with the United States and United Kingdom. Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Confirmed case: isolation of group A streptococci from a usually sterile site (blood, cerebrospinal, pleural, or peritoneal fluid, tissue biopsy, surgical wound); or Probable case: isolation of group A streptococci from a nonsterile website (throat, sputum, vagina, superficial pores and skin lesion), and Clinical indicators of severity: 1. Hypotension: systolic blood stress 90 mm Hg in adults or beneath 5th percentile for age in children, and a pair of. In the presence of four principal standards, Kawasaki disease prognosis could be made on day 4 of sickness.
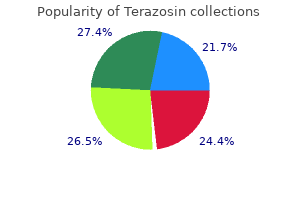
Buy terazosin with amex
Urinary phosphate/creatinine, calcium/ creatinine, and magnesium/creatinine ratios in a healthy pediatric inhabitants. Persistent familial hematuria in youngsters and the locus for skinny basement membrane nephropathy. Inability of community-based laboratories to determine pathological casts in urine samples. Factors affecting spontaneous resolution of hematuria in childhood nutcracker syndrome. Kryger probably the most severe causes of acute scrotal swelling are testicular torsion and incarcerated inguinal hernia, each of which necessitate instant surgical correction. Consequently, a prompt, cautious strategy to a painful or infected scrotum is crucial. The differential diagnosis of scrotal swelling is in depth and varies relying on the age of the patient (Tables 21. The most common causes embrace testicular torsion, torsion of the appendix testis, and epididymitis. The anterior wall of the canal is shaped by the exterior indirect aponeurosis; the posterior wall is shaped by the inguinal ligament and conjoined tendon. The indirect path of the inguinal canal allows for the posterior and anterior partitions to coapt with will increase in intraabdominal stress. The vas deferens could be palpated as a slender, firm, tubular structure in the spermatic twine. Each testis relies on three arteries for its blood supply: the testicular artery, the cremasteric artery, and the deferential artery. These autonomic nerves carry impulses that, with testicular stimulation, produce signs of deep visceral ache and nausea. Onset of pain: Testicular torsion has a really sudden onset and could be precipitated by activity or can occur at rest or during sleep. Epididymitis or torsion of the appendix testis or other testicular appendage typically has a extra insidious onset over the course of days, with progressive ache and swelling. Abdominal signs/symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and belly or inguinal pain are widespread but nonspecific. Urologic signs/symptoms: Dysuria, urinary frequency, hematuria, or penile discharge suggests an infectious process similar to urinary tract an infection, urethritis, or epididymitis. Unusual rashes: Henoch-Sch�nlein purpura may result in vasculitis of the spermatic cord with associated scrotal pain and swelling. In addition, an intensive medical history is crucial and may embody the following: 1. Prior sexual exercise, which might increase the potential of a sexually transmitted an infection. Often an orchiopexy performed for an undescended testis places the testis in a dartos pouch, which might make testicular torsion unlikely in the future. Testis Descent the testes develop within the lumbar region of the stomach cavity between the peritoneum and the transversalis fascia at roughly 7 weeks of gestation. By the 8th week of gestation, the gubernaculum extends from the caudal end of the epididymis through the inguinal canal to insert on the internal wall of the scrotum. The processus vaginalis, a finger-like outpouching of the peritoneum, extends adjacent to the gubernaculum to type the inguinal canal. As the processus vaginalis descends into the scrotum, it carries extensions of the stomach wall layers. The testis usually descends through the inguinal canal into the scrotum before delivery. When the testis reaches the scrotum, the testis and surrounding layers of fascia and tunica vaginalis fuse to the dartos of the scrotum. The processus vaginalis is initially patent, leaving a connection between the scrotum and the peritoneal cavity. Normally, the processus vaginalis obliterates, leaving a residual tunica vaginalis surrounding the testis. Scrotum the scrotum has 2 separate compartments, every containing a testis, epididymis, and distal spermatic cord.
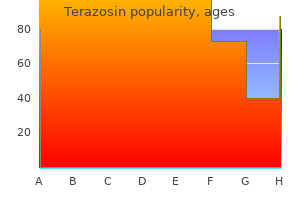
Purchase terazosin 2 mg on line
The most common organisms identified embody Staphylococcus aureus, Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, and streptococcal species. Genitourinary manifestations may include glomerulonephritis (see Chapter 20), ureteritis, renal pelvic bleeding, and acute swelling of the scrotum and spermatic wire. Scrotal wall and testicular involvement has been reported in as much as a third of affected sufferers. Palpable purpura (the attribute pores and skin discovering in HenochSch�nlein purpura) often begin within the decrease extremities and buttock region. Later, the rash could unfold to the scrotum; once in a while, the rash may start on the scrotum. If scrotal swelling and pain precede the event of the characteristic rash, the presentation may be difficult to distinguish from testicular torsion. Sensory innervation to the scrotum contains the genitofemoral and ilioinguinal nerves. Acute Idiopathic Scrotal Wall Edema Acute idiopathic scrotal wall edema is an uncommon entity that accounts for as much as 5% of acute scrotal swelling. Physical examination findings suggesting testicular torsion include marked tenderness, high-riding testis, and absent cremasteric reflex. A varicocele before puberty or on the right facet is a pink flag; abdominal ultrasonography is indicated. Testicular salvage and age-related delay in the presentation of testicular torsion. Colour Doppler ultrasonography replacing surgical exploration for acute scrotum: myth or reality Intermittent testicular torsion within the pediatric affected person: sonographic indicators of a difficult analysis. Accuracy of Doppler sonography in the analysis of acute conditions of the scrotum in youngsters. Trauma to male genital organs: a 10-year review of 156 sufferers, including 118 treated by surgical procedure. Kidney and testicle injuries in group and individual sports: data from the National Pediatric Trauma Registry. Risk elements for progressive deterioration of semen high quality in patients with varicocele. Comparative assessment of pediatric testicular quantity: Orchidometer versus ultrasound. Testicular progress arrest and adolescent varicocele: Does varicocele size make a difference Stromal testis tumors in youngsters: a report from the Prepubertal Testis Tumor Registry. Differentiation of epididymitis and appendix testis torosion by clinical and ultrasound indicators in youngsters. Epididymitis in infants and boys: Underlying urogenital anomalies and efficacy of imaging modalities. An audit of the administration of the acute scrotum in youngsters with Henoch-Sch�nlein purpura. An evaluation of scientific outcomes using colour Doppler testicular ultrasound for testicular torsion. Color Doppler sonography: Its real function in the analysis of children with extremely suspected testicular torsion. A retrospective evaluation of pediatric patients with epididymitis, testicular torsion, and torsion of testicular appendages. There are unique characteristics making historical past and physical examination efficient in narrowing the diagnostic possibilities as seen in Table 22. Collecting info regarding current trauma, medicine exposure, rashes or irritation of the external genitalia, stomach ache, chronic cough, constipation, and malodorous discharge are important in making a analysis effectively. A delicate evaluation relating to the possibility of sexual assault must be made, and an age-appropriate physical examination ought to be carried out noting the presence or absence of other pubertal signs, abnormalities of the vulva or urethra, vaginal discharge, and belly or vaginal plenty. Vaginal bleeding presenting inside the first several days of life is mostly because of estrogen withdrawal.
Trimethylxanthine (Caffeine). Terazosin.
- Preventing dizziness on standing up (orthostatic hypotension) in older people.
- Preventing type 2 diabetes when consumed from coffee or tea.
- Mental alertness.
- Dosing considerations for Caffeine.
- Asthma.
- Preventing gallstones.
- Headache after epidural anesthesia.
- Headache, including migraine and headache following surgery.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Caffeine work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96940
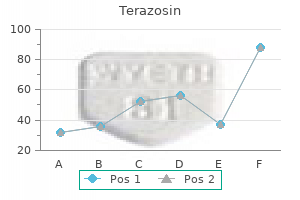
Terazosin 5 mg cheap
Benign paroxysmal vertigo could additionally be confused with seizures as a result of attacks develop suddenly, are accompanied by ataxia, and should trigger the infant or younger youngster to fall. There is pallor, distress, and assumption of a immobile, often supine, position, but no lack of consciousness; older youngsters can recall the event. Older children can establish signs of nausea and vertigo and are less likely to be thought to be experiencing seizures. The situation is intently associated to migraine, with many shared symptoms and the later improvement of extra typical migrainous headache. This unusual syndrome could resemble the cryptogenic type of childish spasms at onset, with bilateral myoclonic jerks developing in a beforehand regular infant. However, this is a benign, in all probability nonepileptic situation occurring in infants 3-8 months of age and disappearing after a interval of weeks or months. The pattern of myoclonus may differentiate it from childish spasms, together with predominant involvement of the top, neck, and higher limbs with adversive head actions or tremors with out involving the decrease limbs. These abnormal movements could necessitate monitoring to establish a nonepileptic prognosis. Alternating hemiplegia of childhood is a rare syndrome of episodic hemiplegia that usually manifests in infancy with the next diagnostic criteria: 1. Recurrent episodes of fluctuating hemiparesis or hemiplegia affecting either side of the body and disappearing throughout sleep three. Other paroxysmal phenomena: tonic seizures, dystonic posturing, choreoathetosis, nystagmus, and other paroxysmal oculomotor disturbances; and autonomic dysfunction, occurring throughout or between hemiplegic episodes four. Progressive cognitive and neurologic deficits the pathophysiologic mechanism remains unknown, though there are reviews of mitochondrial dysfunction in some cases and an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance in others. The differential prognosis contains paroxysmal choreoathetosis and dystonia syndromes, familial hemiplegic migraine, transient ischemic assaults related to cerebral vascular abnormalities such as moyamoya illness or cardiac emboli, mitochondrial disorders, hyperviscosity, sickle cell anemia crises, inherited problems of metabolism (pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency and Leigh disease), and epileptic seizures with postictal paralysis. There have been case reports of a similar-appearing disorder with nocturnal paroxysmal events of flaccid hemiplegia lasting up to several hours at a time. The key differentiating elements are that these kids are primarily normal previous to analysis, the events occur during sleep, and the children seem to outgrow these spells by midchildhood without significant long-term neurologic sequelae. Febrile convulsions are widespread and are defined as seizures occurring between the ages of 6 months and 5 years in affiliation with a fever in the absence of intracranial an infection. The highest incidence of febrile convulsions occurs between 1 and a pair of years of age, and 85% of febrile convulsions occur before the age of four years. The seizures are often temporary with generalized clonic or tonicclonic motor involvement with none postictal paralysis or a chronic postictal state of confusion or drowsiness. The seizures usually happen well throughout the first 24 hours of a febrile sickness, not essentially when the fever is highest; they may be the first indication of sickness. Complicated febrile convulsions are outlined as these lasting longer than 15 minutes, recurring throughout a single febrile sickness, having unilateral or focal features, or adopted by postictal paralysis. Seizures occurring late in a febrile illness should elevate suspicions of encephalitis, brain abscess, or meningitis. The preliminary investigation must embrace a search for the purpose for the febrile illness. Herpes simplex encephalitis in particular must be considered in children presenting with evidence of encephalitis and focal seizures. However, if the history is according to a febrile seizure, the child is in the appropriate age vary and is developmentally normal, a fever has been documented, and an apparent source of infection has been found, in depth investigations are pointless. Treatment of a kid nonetheless in convulsion on arrival at the hospital should embrace prompt attention to protection of the airway and circulation. Nasal or rectal diazepam or intravenous lorazepam must be administered if the kid has been seizing for more than 10 minutes. The household must be advised that future fevers with temperatures above 38�C (100. However, approximately 30% of febrile convulsions recur in future febrile sickness, and the mother and father ought to be warned of this. Recurrence is most probably in the first 6-12 months after the preliminary febrile convulsion. Other elements that improve the chance of recurrence are onset at a younger age, preexisting neurologic abnormalities, and household history of epilepsy or febrile convulsions. Most authorities would advise no treatment for almost all children with febrile convulsions. For children with recurrent prolonged febrile seizures, rectal diazepam could be thought of as an abortive therapy.
Generic terazosin 1 mg
Infantile esotropia is outlined as convergent strabismus with onset throughout the 1st 6 months of life. Transient crossing or divergence of the eyes is widespread in newborns and is probably not significant except it persists beyond three months of age. The child might alternate fixation (cross fixate) in which case the visual acuity is often good in both eyes. The incidence of childish esotropia is lower than 1% among neurologically normal infants. Early correction of infantile esotropia might result in full or nearly full restoration of normal binocular perform, a outcome not believed to be obtainable with correction of misalignment at older ages. Note that the wide nasal bridge and outstanding epicanthal folds create the phantasm of an esotropia. The corneal light reflexes are centered in each eye; subsequently, the eyes are straight. Early detection and prompt referral of infants with suspected esotropia are indicated. A second category of esotropia happens in children whose eyes are initially straight however start to cross, normally intermittently at first, at 1-3 years of age. These youngsters have excessive hyperopia and an abnormal relationship between lodging and convergence. Treatment consists of correcting amblyopia and offering spectacles to right hyperopia, thereby modulating the quantity of accommodation required by the child. Bifocal spectacles may be essential for some forms of accommodative esotropia. Esotropia brought on by paralysis of a lateral rectus muscle, a 6th cranial nerve palsy, occurs rather more frequently in kids than in infancy. An older baby may current with complaints of diplopia or a face turn or closure of 1 eye to avoid diplopia, whereas a younger youngster may present with only the esotropia due to rapid improvement of suppression to eliminate diplopia. Infantile exotropia presents as a big deviation of the eyes previous to 6 months of age. It is, nevertheless, generally related to craniofacial problems or neurologic impairment. Surgery could also be done early in life, but these patients are less more doubtless to acquire good binocular imaginative and prescient than infantile esotropes. Because the child maintains the ability to hold the eyes aligned a part of the time, amblyopia is uncommon. Diplopia is prevented by energetic cortical suppression of enter from the portion of the retina of the deviated eye that overlaps the central view of the fixating eye. When the eyes are straight, the child generally maintains regular binocular perform, together with stereopsis. Treatment options embody part-time patching, additional minus power spectacles in sufferers with myopia, orthoptic workouts, and surgical procedure. A small vertical deviation in affiliation with a bigger quantity of horizontal strabismus, nevertheless, is common, and is managed along side the horizontal deviation. The deviation is totally managed with glasses at both distant (middle) and near (bottom) fixation distances. The incidence and diploma of myopia enhance with age, especially during development spurts, as in adolescence. There is a posh interplay between genetic and environmental components in the development of myopia. The incidence of myopia varies with ethnicity and geographic regions and has been increasing in prevalence over the previous 50 years. There have been a number of genetic markers linked to myopia but the growing frequency among younger generations suggests environment performs an essential role. The increase in prevalence from 10-90% in some populations is a public well being concern, particularly with high myopia. Myopia can be related to elevated danger of retinal detachment, early cataract, and glaucoma. This may end up in decreased imaginative and prescient even with spectacle or contact lens correction.

5 mg terazosin sale
Lavage returns which would possibly be shiny purple point out important ongoing bleeding; pink-tinged or brown flecks within the solution indicate less vital or minimal bleeding. Maintaining a gastric pH of more than 4 is taken into account standard remedy for higher gastrointestinal mucosal bleeding. This may be achieved with both H2-receptor antagonists or proton pump inhibitors. Vasoactive Agents In patients with suspected variceal bleeding, a continuous infusion of octreotide could additionally be began. This agent reduces splanchnic blood circulate with minimal disturbance to different organs. It is safer than vasopressin however has not been shown to have profit in nonvariceal bleeding. Customarily, a bolus of octreotide (1-2 �g/kg) is given over 5-10 minutes, and that is adopted by a steady infusion of 1 �g/kg/hr, though higher doses may be required. The infusion might help management the bleeding till definitive remedy (banding or sclerotherapy) is carried out. Endoscopic Modalities Most patients with gastrointestinal bleeding will endure upper and/ or lower endoscopy for definitive analysis and therapy. For sufferers with mucosal lesions, such as ulcers or bleeding polyps, there are a number of therapeutic interventions available. Injection with a diluted epinephrine solution, thermal coagulation, laser photocoagulation, and endoscopic clips can be used to stop energetic bleeding. For patients with colitis, colonoscopy is used primarily to confirm prognosis and extent of illness. Variceal banding is the preferred method for treating bleeding esophageal varices. Ideally, the banding takes place after good control of acute bleeding, affording the endoscopist an unobstructed view of the varices. Side effects of this therapy are minimal, and the procedure is repeated weekly to month-to-month till the varices are obliterated. Sclerotherapy is also effective in controlling the acute bleeding from esophageal varices and may be carried out weekly to month-to-month until the varices resolve. In young children whose upper esophageal sphincter is too small for the endoscopic banding device to move, sclerotherapy will be the only possibility. Surgical intervention is a definitive therapy for lots of the anatomic anomalies inflicting gastrointestinal bleeding and could also be performed at the side of endoscopy to establish the lesion. Interventional Radiology Selective embolization throughout angiography can be used to treat vascular malformations and to management bleeding from ulcers. The fee of issues from angiography is 2%, whether the procedure is diagnostic or therapeutic. In sufferers with intrahepatic portal hypertension with bleeding from gastrointestinal websites inaccessible to sclerotherapy or banding, coiling of varices or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting could also be helpful. Approach to gastrointestinal bleeding begins with guaranteeing hemodynamic stability of the patient while acquiring an intensive history and physical examination to assist decide upper versus lower supply of bleeding. Laboratory, radiologic, and endoscopic analysis are used for affirmation of prognosis and potentially treatment. Vomiting-induced hematemesis in children: Mallory-Weiss tear or prolapse gastropathy Use of capsule endoscopy in analysis and management of pediatric patients, based on meta-analysis. Extraintestinal manifestations of pediatric inflammatory bowel illness and their relation to disease kind and severity. Predictors of clinically vital higher gastrointestinal hemorrhage among children with hematemesis. Juvenile polyps and juvenile polyp syndromes in children: A clinical and endoscopic survey. Standards of Practice Committee of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Contribution of intraoperative enteroscopy in the administration of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Prevalence and end result of allergic colitis in healthy infants with rectal bleeding: A potential cohort research.
Discount 2mg terazosin with visa
The full-term infant reveals a traction response with minimal head lag, and when the sitting posture is attained, the head could additionally be held erect momentarily after which falls ahead. By age three months, there should be no head lag, and the pinnacle should be aligned with the plane of the again as the child is pulled to sitting. The hypotonic toddler might assume uncommon postures in the presence of joint hyperextensibility. With the toddler in a semireclining position, the hand is pulled throughout the chest toward the opposite shoulder and the place of the elbow is famous. Stretching of the quadriceps muscle (agonist) will lead to leisure or inhibition of the hamstring muscle (antagonist). An toddler with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy who was initially hypotonic at the time of delivery was famous to be hypertonic at eight months with a standard ventral suspension response as evidenced by the flexibility to maintain the top above horizontal (C). Note the frog-leg posture of the decrease limbs and inner rotation ("jug-handle") at the shoulders. B, A 1-year-old toddler with frog-leg posture, exterior rotation at shoulders, intercostal recession, and normal facial expressions. A 6-week old toddler with marked weakness of the limbs and trunk giving the attribute inverted "U" appearance on ventral suspension (C) and pullto-sit (D). The response to axillary suspension allows assessment of generalized and shoulder girdle tone. The infant is held underneath the arms, lifted, and suspended from the axillae without the thorax being grasped. The response to ventral suspension permits assessment of tone of the trunk, neck, and extremities. A normal infant holds the pinnacle erect and the back straight and holds the extremities with some flexion at the elbows, hips, knees, and ankles. A full-term neonate makes intermittent attempts to hold the pinnacle straight, maintains the again straight, and might flex the limbs. In addition, causes of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita must be thought of (Table 29. If the child is markedly weak, the examiner should verify to see whether the mother can also be weak (proximal muscle weakness, ptosis, ophthalmoparesis) or whether or not she shows myotonia (on hand grip or to percussion). If either is true, then transplacental-derived transient neonatal myasthenia gravis or myotonic dystrophy, respectively, is a chance (Table 29. Brain harm resulting from asphyxia, hypoxia, or ischemia is an important reason for neonatal neurologic morbidity. Tissue oxygen deficiency is presumed to underlie the neurologic injury brought on by hypoxic-ischemic insults. Asphyxia denotes an impairment in fuel change, which ends not solely in a deficit of oxygen in blood but also in an excess of carbon dioxide and thereby acidosis. Furthermore, sustained asphyxia often results in hypotension and ischemia, which is consistent with the probably predominant importance of ischemia as the final frequent pathway to mind injury. Asphyxia is the commonest scientific insult resulting in mind damage through the perinatal period. Evidence of hypoxic-ischemic damage to the neonatal nervous system is mirrored by a constellation of indicators noticed early after delivery. The asphyxiating event or occasions could happen at any level in the antepartum, intrapartum, or postpartum durations. Maternal cardiac arrest or hemorrhage resulting in transplacental and fetal hypotension represents such prenatal insults. Postpartum difficulties are discovered extra generally in premature than in full-term infants. Nonetheless, if the hypoxic-ischemic injury has occurred well in advance of parturition, it might be asymptomatic in the neonate. Turning head to 1 aspect when supine elicits extension of arms and leg ipsilateral to facet that head is turned and flexion of reverse arm and leg. Persistence past 2 months would possibly suggest abnormal improvement of contralateral motor cortex.
Discount 1mg terazosin mastercard
These sufferers have a tendency to develop nephrocalcinosis and nephrolithiasis, which ends from the excretion of huge quantities of calcium, mixed with an alkaline urine pH and hypocitraturia. In addition to the poor H+ secretion, these patients are unable to increase ammonia genesis. Because the distal acidification mechanisms are intact, these patients can lower the urine pH to less than 5. In some sufferers, there may be an increase in urinary calcium excretion, however as a end result of citrate excretion is normal, nephrocalcinosis is unusual. Low Normal or near regular High 10-20 <40 Low No Gastrointestinal Loss of Bicarbonate Diarrhea is the commonest explanation for non�anion hole hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis in kids. The diploma of dehydration should be assessed and acceptable fluid resuscitation ought to be given, which ought to help right the acidosis. Patients with Fanconi syndrome must be evaluated for cystinosis, the commonest explanation for Fanconi syndrome in children. The price of formation of ketone our bodies, principally -hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, exceeds the capability for his or her peripheral utilization and renal excretion. Accumulation of ketoacids (both of that are relatively robust acids and dissociate quickly into H+ and the ketoacid anions) ends in metabolic acidosis. The loss of ketoacid anions in urine will increase the urinary losses of Na+ and K+ because the accompanying cations. During treatment of metabolic acidosis, the first effort should give attention to the administration of the underlying situation. During the correction of acute metabolic acidosis, specific attention must be paid to guarantee an applicable potassium balance. During an episode of metabolic acidosis, potassium shifts from the intracellular house to the extracellular house in trade for H+, and thus the presence of a total physique potassium deficit will not be appreciated. Chronic metabolic acidosis slows linear growth and interferes with bone mineralization. Treatment of hypovolemia improves tissue perfusion and renal operate thereby increasing the excretion of organic acids. Under normal circumstances, lactate is formed in comparatively small quantities and is additional metabolized by the liver. Pathologic conditions related to either local or systemic hypoxia or ischemia, hypotension (shock), impaired oxidative metabolism, or impaired hepatic clearance may cause vital lactic acidosis. The diagnosis of lactic acidosis must be thought of in all forms of elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis. Most patients with inborn errors of metabolism that trigger a metabolic acidosis present within the neonatal period or shortly thereafter. Organic acidemias, aminoacidopathies, disorders of fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial problems, and defects in carbohydrate metabolism are associated with acidosis. Associated presenting signs and symptoms may embody vomiting, failure to thrive, lethargy, seizures, developmental abnormalities, hepatomegaly, and elevated blood or urine levels of a specific metabolite. Some of those issues shall be detected by the state new child screening protocols. In distinction, urea cycle issues through the 1st few days of life manifest with respiratory alkalosis due to stimulation of the respiratory middle by elevated ammonia levels. A number of toxic agents may be associated with elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis; these include salicylate intoxication, ethylene glycol (a component of antifreeze), and methanol. Carbon monoxide, cyanide poisoning, or methemoglobinemia induces hypoxic acidosis. Classically, salicylate intoxication is described as causing respiratory alkalosis (stimulation of the respiratory center), adopted by elevated anion hole metabolic acidosis (accumulation of salicylic acid itself and lactic acidosis on account of uncoupling of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation). Nausea, tinnitus, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, and prolonged prothrombin time are other related features. Alkalization of the blood and urine with sodium bicarbonate is beneficial despite the potential problems associated with its use in acute metabolic acidosis. Alkalization of the plasma decreases the diffusion of salicylate into the central nervous system, and alkaline urine improves renal excretion.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Terazosin
Gamal, 27 years: The "first and worst" headache, which raises concerns for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in adults, is commonly due to a febrile sickness associated to upper respiratory tract infection in kids.
Chris, 42 years: They are additionally a supply of great concern to dad and mom, who fear the potential for malignancy.
Murat, 26 years: The onset of signs is insidious and usually happens during late childhood or early adolescence.
8 of 10 - Review by K. Renwik
Votes: 61 votes
Total customer reviews: 61


